Wisdom teeth (eights, third molars) are the last units on each side of the tooth row. They are the last to erupt when the dentoalveolar system is fully formed. And in most cases, their appearance causes a lot of problems. Since they often do not have enough space in the row, they grow incorrectly: at an angle, sideways, horizontally, interfere with neighboring units, traumatize the mucosa of the cheeks, tongue.
Whether it is necessary to remove wisdom teeth – depends on the clinical situation. The doctor will not remove the third molars “just in case”. There must be medical indications for this. The anatomy of the eights is more complex, they are the largest units in the row with a developed root system. Although they belong to the chewing group of teeth, they do not take part in the process of chewing, this function of the units is weakened or absent. The primary function of the third molars is to keep the teeth in the row from moving apart.
What problems can arise
- In almost 80% of cases, the eruption of third molars is accompanied by various purulent-inflammatory processes. A mucous hood is formed over the erupting unit, a pocket is created around it, where bacterial plaque accumulates, food residues, which leads to purulent inflammation – pericoronaritis.
- Often the eights grow towards the tongue, cheek, palate, constantly traumatizing the mucosa, delivering a lot of painful, discomforting sensations. Chronic trauma to soft tissues can lead to the formation of ulcers, erosions, the development of leukoplakia (hyperkeratosis) – on the traumatized area of the mucosa becomes more dense. If the cause (traumatic tooth) is not eliminated, there is a risk of neoplasm (including malignant).
- Between 8 and 7 (on the contact surfaces) a carious cavity is formed where food is constantly clogged, contributing to the rapid development of caries. The carious process affects not only the eight, but also the 7 molars, which are important for the dentoalveolar apparatus. In case of interdental caries it is necessary to remove the wisdom tooth, and the seventh molar should be treated qualitatively.
- Sometimes the eighth molar is located horizontally in the gum, rests on the root of the neighboring tooth, traumatizes it, provokes the formation of a cyst. Such pathology in the worst case scenario can even lead to resection of the jawbone. As a result of a long asymptomatic period, cysts can acquire significant size, damage the surrounding bone tissues, neighboring units.
- Wisdom teeth can exert serious pressure on neighboring units, shifting them out of place. This pressure is transmitted to all teeth, provoking deformities of the row, bite disorders, periodontal disease.
In what cases the wisdom tooth is extracted
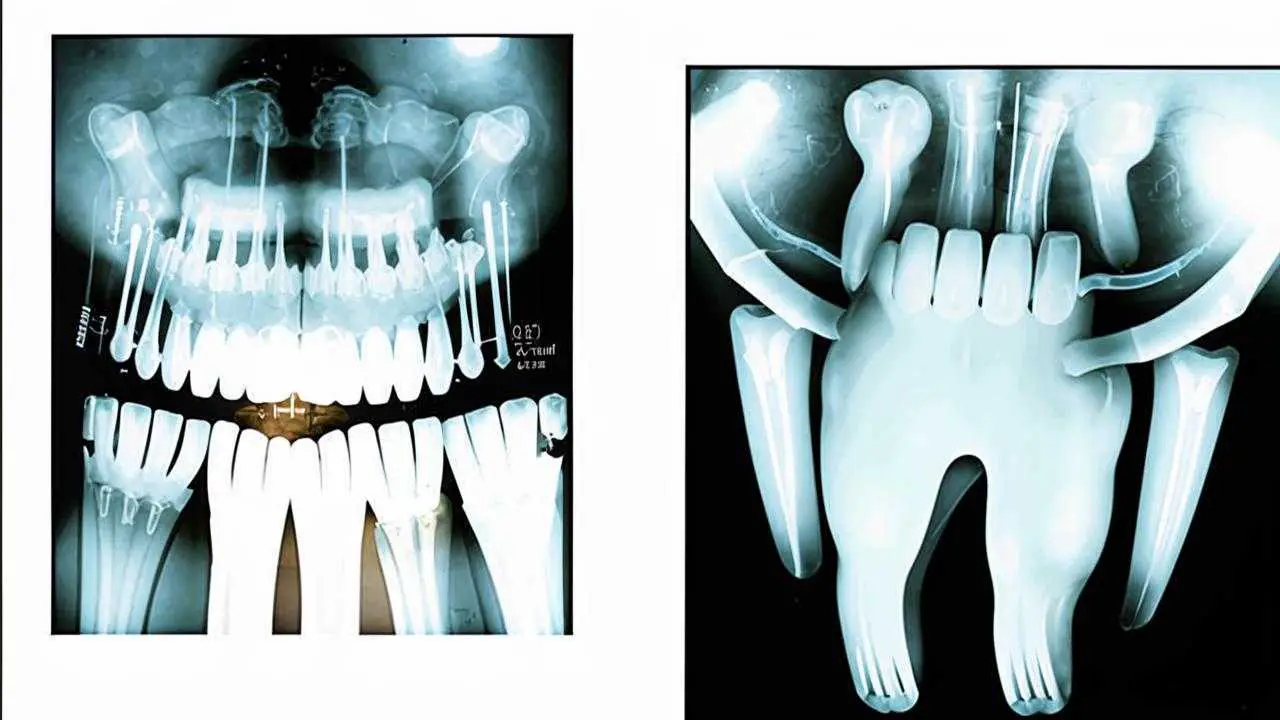
The most common indication for surgical removal of third molars is their abnormal position or difficult eruption. In many cases, they remain inside the jawbone for a very long time, having difficulty erupting to the surface, causing many problems. In these clinical situations, the oral surgeon performs a rather complex surgery to extract the tooth unit from the bone tissue.
The reasons why wisdom teeth are removed are many. A direct indication for surgical extraction of the eight is:
- hygiene of the third molars is difficult or impossible;
- decay, crown decay;
- retained molars (not erupted partially or completely);
- displacement of teeth in the row due to the growth of eight teeth;
- dystopia (misalignment of the eight in the row) or traumatic occlusion;
- Difficult access when treating neighboring units;
- inclined positioning, contributing to distortion, destruction of neighboring units;
- eruption beyond the boundary of the tooth row;
- wisdom tooth roots growing into the maxillary sinus;
- eruption of the eight caused complications (facial neuralgia);
- incomplete eruption with the presence of a hood of gingival mucosa.
Often the extraction of wisdom teeth is carried out for orthodontic indications, when due to their abnormal position begins to shift the entire row – shifting quadruplets, incisors, forming crowding of the front group of dental units. When braces are removed wisdom teeth to reduce the period of correction, to exclude complications if the eights begin to erupt during treatment.
Why remove a wisdom tooth
Third molars are rarely retained – they deteriorate early or extraction is necessary for the proper functioning of the tooth row. Most dentists prefer to remove the abnormal 8 before they can seriously damage the health of the jaw (especially the lower jaw) to the entire row.
A wisdom tooth should not be extracted when the 6th and 7th molars are missing. Contraindication to extraction is inflammation of the periodontium, root, bone or gingiva, because there is a risk of spreading and aggravation of the pathological process against the background of the postoperative wound. The limitation to surgical extraction of third molars is:
- 8 location in the area of malignant formation;
- pregnancy;
- hypertension of II-III degree;
- heart attack, stroke suffered less than 3 months ago.
All operations, including dental, in these cases are carried out after consultation with the patient’s attending physician.
When it is possible not to remove them
Modern dentistry clearly formulates the attitude to the eight – it is possible not to remove wisdom teeth on condition that:
- there is enough space for them to erupt;
- erupted molars occupy anatomically correct position, do not harm neighboring units;
- there is nothing preventing the treatment of the eight;
- third molars do not complicate hygienic care of teeth and gums;
- the wisdom tooth is needed as a support for the fixation of a bridge or other orthopedic system (if there is no 7).
If the third molars are affected by caries, they in any way interfere with other units in the row or the process of chewing, regularly traumatize the mucosa – they must be removed. In this matter, world dentistry is ruthless, the presence of eights is allowed exactly until they do not harm the health of the dentoalveolar system and do not violate its functionality.
Whether wisdom teeth can be treated
If the third molars occupy the correct anatomical position, with a timely appeal to the doctor, the eights are amenable to treatment – medication, therapeutic. The doctor decides in favor of treatment after a comprehensive assessment of the clinical picture. Filling is carried out according to the standard protocol.
Is it possible to remove several wisdom teeth at once
It is possible to remove two wisdom teeth at once, but it is a certain stress for the body. More often such an operation is performed when it is necessary to remove the eights on one side (1 upper, 1 lower). This is done to preserve normal nutritional function. During surgical extraction, a powerful anesthesia is applied, so the operation is painless.
But after the removal of a large molar, a fairly extensive wound remains. Until it heals, the load on the operated area should be minimized, respectively, you can chew on the side opposite the hole. If you remove both eights on the upper or lower jaw, it will be problematic to eat. And this affects the digestive system, the state of immunity, and general health.
Treatment of complications in the growth of eights
The most common complication in the growth of the eights is pericoronaritis (formation of the gum hood). Molar erupting has to overcome many obstacles: jawbone, periosteum, periodontal tissues. In case of long, complicated eruption, a specific mucous canopy (hood) is formed over the molar. Under it, bacteria, food particles penetrate, which becomes the cause of inflammation.
If the coronary is not treated, the consequences will be serious, the inflammation will spread to the periosteum, the jawbone. This is fraught with the development of periostitis, osteomyelitis, suppuration of tissues with the formation of phlegmon, cysts, fistulous passages. Nearby tissues may be affected, inflammatory ENT pathologies (otitis media, maxillary sinusitis) may occur.
Treatment of pericoronaritis is surgical, involves excision of the mucous hood. The operation opens access to the growing eight. The doctor removes the affected tissues, carefully treats the surgical area, evaluates the clinical picture. According to the situation, decides whether to remove the eight or help the molar to erupt finally, taking the right place in the row.
How to ease the eruption of the wisdom tooth
Relieve pain, reduce inflammation, will help to take non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: Ibuprofen, Nimesulide, Bofen, Dexalgin, etc. Applications of local anesthetics, rinses with Miramistin, Chlorhexidine solution help well. Dental gel (Holisal, Camistad, Dentinale Natura, etc.) will help soothe the inflamed gum, reduce swelling.
Rinses with decoctions of medicinal herbs – oak bark, yarrow, chamomile – will relieve the condition. Reduce inflammation, swelling, soreness will help gargle with a solution of baking soda (1 tsp. per glass of water), applications with propolis. What categorically can not do – to warm the inflamed gum.
If complications occur during the eruption of the wisdom tooth, do not self-medicate. It is necessary to seek medical help. After a comprehensive diagnosis, the doctor will decide whether to remove the wisdom teeth. If the temperature has risen during eruption, there are signs of intoxication (general weakness, headache, chills, etc.) you should immediately go to the dentist to avoid abscess formation and other serious consequences.