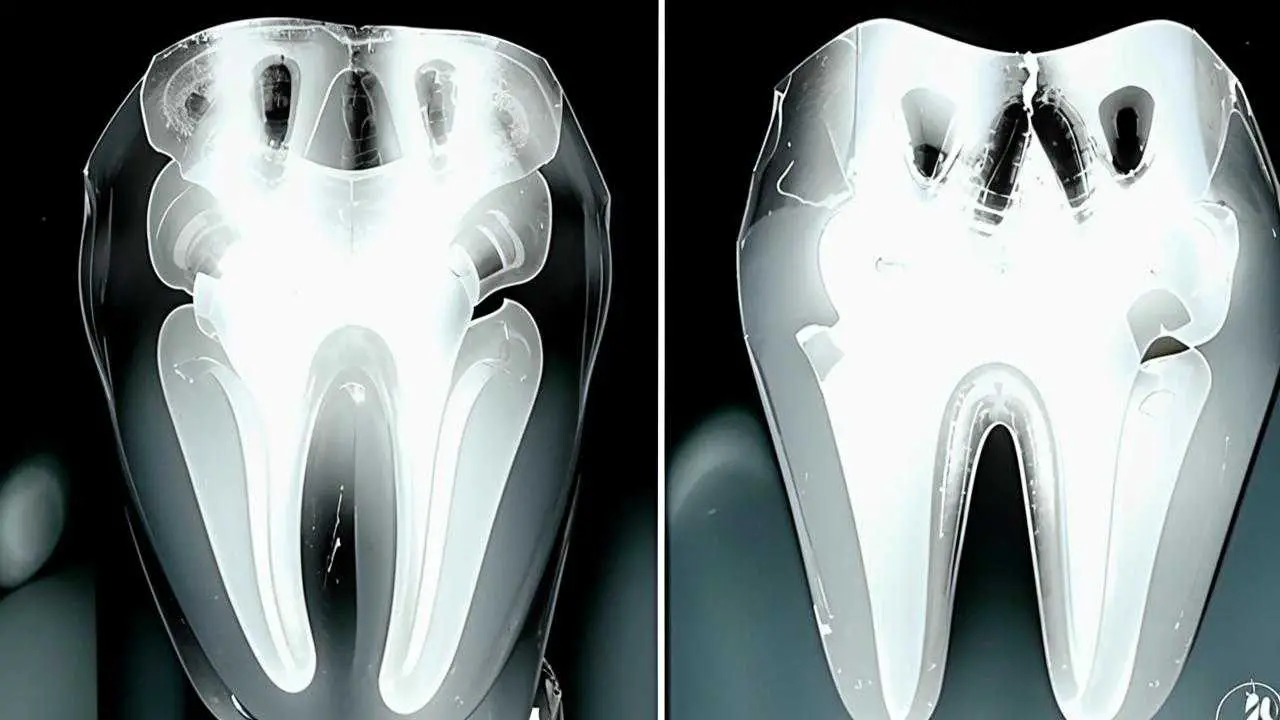
Wisdom tooth is the 8th tooth in a row (eight) or 3rd molar, its eruption period is 17-25 years. It is a large molar, more often with a complex root system. Features of its development and growth in most cases become the cause of various dental problems. Although the structure of the eight is characterized as an ordinary molar, its chewing function is practically absent. If the wisdom tooth hurts, it is rarely saved. The eight is destroyed early, often erupts already with carious lesions, grows at an incline or in a horizontal position.
How to understand that the wisdom tooth hurts?
Eights erupt much later than all the other teeth in the row, when the dentoalveolar apparatus is fully formed, and there is simply not enough room for the newcomer. Because of the density of the gum and bone tissue, eruption is quite painful, accompanied by inflammation of the gum, damage to neighboring units. Pain during the growth of the wisdom tooth is quite specific:
- It spreads along the jaw, gives in the temple, neck, head, head, ear, throat;
- swelling around the eight, redness of the gum tissue;
- pain and soreness in the throat, difficulty swallowing;
- numbness of the jaw and pronounced pain tells that the 3rd molar grows crookedly, traumatizing the jaw nerve;
- it is difficult to open the mouth, especially if the wisdom tooth grows in the opposite side of the jaw.
Each of these symptoms indicates a problem with the 3rd molar. Temporarily relieve wisdom tooth eruption pain with an analgesic. If the eights grow crookedly, the bite is disturbed, the cheek and gum are traumatized, they are formed in the bone tissue, not erupting to the surface or appearing only partially – they must be removed.
Why a wisdom tooth can hurt
- Irregular eruption – retined teeth formed in the jawbone, not erupted at all or partially, can be located horizontally, vertically. When the eight is located laterally, it exerts strong pressure on the neighboring units, provoking acute pain.
- Gum hood – dense gum can prevent eruption, a “hood”of mucous tissue is formed over the wisdom tooth. Under it, bacteria begin to accumulate, food particles, unremoved when brushing teeth. This area is constantly traumatized, inflamed, painful. Acute inflammatory process often develops into purulent.
- The molar is turned around the axis – the more pronounced the turn, the stronger the impact on the dental nerve, which causes pain in the molar itself, the neighboring unit or the entire jaw.
- The cheek hurts because of the wisdom tooth, if it grows to its side. Soreness increases when chewing, the cheek mucosa is constantly traumatized, inflamed.
- Caries – the localization of the 3rd molar makes it difficult to care for it, it is often cut already with carious lesions of hard tissues, which causes pain. The sensitivity of the tooth increases, it reacts painfully to temperature and chemical stimuli.
- Cyst – due to systematic traumatization of the gum tissue, the molar itself, a cystic formation can form at the neck. Wisdom tooth cyst is often accompanied by serious complications – inflammation of peri-dental tissues, pericoronaritis, abscess, destruction of bone tissue.
Also the reason that the wisdom tooth began to hurt are various dental pathologies – pulpitis, periodontitis (acute, chronic), periodontal disease. Removal of the eight is not always justified, the doctor decides this question individually, depending on the clinical picture. First, a comprehensive diagnosis is carried out, the doctor determines the location of the roots, assesses the condition of the jawbone, the gum around the eight, the entire dentoalveolar apparatus.
Indications for removal
- Pathological eruption of the eight (partial or complete retention, dystopia), accompanied by pain, chronic inflammation of the gum, destruction of neighboring molars, bite disorder, damage to the jaw joint and other problems;
- 3 molars erupted outside the tooth row, leading to crowding;
- impossibility to perform treatment or prosthetics due to limited access to the tooth unit;
- presence of complications – cysts, granulomas, periostitis, periodontitis;
- orthodontic treatment – the eights must be removed if they interfere with the installation of a corrective appliance, do not allow the teeth to take the correct position when correcting the bite.
When it is recommended to keep an eight
- The 6th or 7th molar is missing;
- The wisdom tooth occupies an anatomically correct position and does not harm other units;
- The 3rd molar supports a bridge or other prosthetic structure;
- an eight is subject to treatment.
When do I need a doctor’s help?
If the eight is painful, it is necessary to immediately consult a dentist. Consultation with a specialist is also necessary in case of pain of uncertain etiology – squeezing, spilling over the entire jaw, occurring when chewing, opening the mouth. After examination and diagnosis, the doctor will decide what to do with the molar further. If the growth of the wisdom tooth is accompanied by swelling, redness of the gum, acute pain, the doctor will prescribe anti-inflammatory therapy.
With difficult eruption due to the gingival hood, an operation will be performed to excise it, medication therapy will be prescribed.
Possible consequences and complications
Due to progressive inflammation, serious complications can occur, up to the destruction of the jawbone. Any self-treatment or folk methods are out of the question. Ointments, gargles, uncontrolled medication will only aggravate the situation. They can temporarily alleviate the condition, but will not eliminate the cause of pain.
Methods of wisdom teeth removal
Tactics of intervention depends on the location of the 3 molars, the degree of exit to the surface of the gum, the number of roots, their entanglement, the position of neighboring teeth. The removal of the eights on the upper jaw is easier than on the lower jaw. This is due to the structure of the jaw tissue – the maxillary bone is more loose, air-bearing, the mandibular bone is more massive, dense. In addition, mandibular eights tend to have more tangled and developed roots.
According to the clinical presentation, extractions come in simple and complex. Simple is performed like any other extraction – the molar is swung with forceps and extracted from the hole. The complex technique includes:
- incision of the gum;
- drilling out the molar or sawing it into fragments;
- removal of each fragment in turn;
- suturing of the wound.
Sutures are removed on the 5th-7th day after the intervention (self-absorbable suture material can be used). The operation is performed under local anesthesia, it is possible to remove under sedation (in medication sleep).
Treatment of the wisdom tooth in pregnancy has its own nuances. Usually, the doctor is limited to conservative therapy aimed at eliminating pain, inflammation. Removal, if possible, is performed after childbirth. Surgery is carried out on strict indications, if the inflammation has become purulent, threatens the health of the mother and child. For anesthesia use special drugs that are safe for the fetus.
In the RUTT Clinic, wisdom tooth extraction with a complex root system and location is performed by experienced maxillofacial surgeons. This excludes surgical complications – extensive trauma to the bony structures of the jaw, perforations, wandering root remnants, postoperative fistulas, osteomyelitis, etc. Only maxillofacial surgeons have enough skill and experience to perform such interventions without complications.
Recovery after surgery
In itself, the removal of the eight is painless, since it is carried out under anesthesia. But due to traumatization of the gum, bone cavity, after the termination of the action of the anesthetic, a few days of painful eight, or rather, peri-dental tissues. Painful sensations after a simple removal usually pass on the 2-3 day, after a complex – may persist for about a week. On the 2-3 day swelling increases, which in 2 days subsides, the pain subsides. After the intervention, the doctor gives recommendations on care, nutrition, lifestyle, prescribes drug therapy – antibiotics, analgesics, anti-inflammatory, anti-histamines.
What can relieve pain
If the gum at the wisdom tooth hurts a lot, a tablet of Ibuprofen, Nimesulide or another analgesic from the group of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) will relieve the condition. Well help applications with local anesthetic, gargling with a solution of Miramistin, Chlorhexidine. Analgesic gel Holysal will soothe the irritated gum, reduce swelling. At home, decoctions of herbs (sage, oak bark, calendula, chamomile), rinsing with a solution of baking soda (1 tsp. of baking soda per glass of warm water) will help to relieve toothache for a while, reduce inflammation.
If the pain does not subside on the 5th-7th day, but on the contrary, it increases, other alarming symptoms have joined – pronounced swelling, putrid breath, purulent discharge from the wound, temperature rise to 38℃ and above, headache, weakness – you should immediately go to the doctor. Such signs indicate the development of complications and require urgent medical attention.