Thanks to advances in dentistry, it is possible to restore a tooth row for almost any defect. The main thing is to choose the right denture method for your specific case. A qualified dentist will be sure to suggest the best dentures for your clinical case. Dentists have a lot to choose from – prosthetics is constantly evolving, new materials, methods and technologies are emerging.
Varieties of dentures
Denture restorations can be removable, fixed or fixed. Most often, the choice depends on how many teeth need to be restored. Therefore, each group has its own varieties of designs.
Removable prostheses
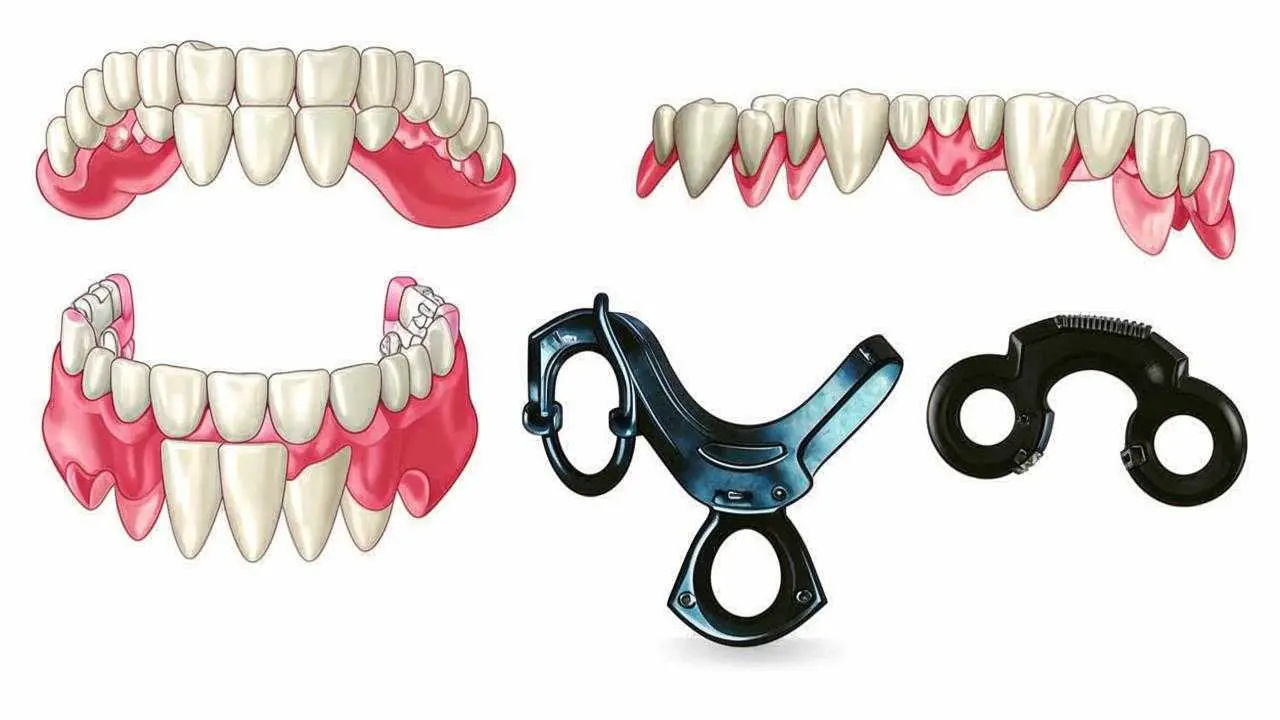
Most often, this type of prosthetics is used in the absence of a large number of teeth or complete adentia. Depending on this, removable dentures can be full or partial. Both consist of a base and artificial teeth. Partial dentures have anchoring elements.
Complete
The best removable dentures are those that fit tightly to the palate, repeating its relief. Removable structures are held due to the vacuum effect. When the denture is put on, it presses on the mucosa, forcing air out of the base. As the mucosa returns to its shape, it prevents the air from returning. A pressure difference and valve effect occurs. On this principle, a towel hook is attached to the wall. This is the basic method. It works well when the design is installed on the upper jaw. There the area of contact is large, the vacuum volume is sufficient to hold the structure. When installed on the lower jaw, there is not enough space, for better fixation use additional means: gels, creams and powders. The most common prostheses in the complete absence of teeth – plate.
Partial
If there are saved teeth, then partial restorations are used. They can be lamellar and burettes. The latter are rapidly replacing the platters. Clip-on structures are convenient removable dental prostheses on a metal or hard plastic arch, on which crowns are fixed. They are attached to the supporting teeth using different types of locks.
The advantage of bracket constructions is that, thanks to the arch, the chewing load is distributed evenly. Part of it falls on the gum, protecting the teeth from rapid destruction and slightly slowing down the loss of bone tissue.
Methods of attachment:
- Clammers. These are hooks that are fixed to the arch and help with retention by gripping the tooth tightly.
- Attachments. Locks that snap into place and hold the structure in place.
- Telescopic crowns. The most reliable, aesthetic, but also the most expensive method of anchoring. On the inner crown is put on the outer crown, which is fixed on a buregel.
The disadvantage of the burettes is one – metal parts can cause allergies. But even here the technologists who develop materials for prosthetics, offered a way out.
Quadrotti dentures
The Italian company Quattro Ti has proposed a new polymer for restorations. It’s called Dental D. It is stronger than metal, but much lighter and does not cause allergies. This restoration has a very narrow palatal bridge. It does not block the taste buds, fits snugly and does not give the feeling of a foreign object.
The new polymer does not cause galvanization, is resistant to temperature fluctuations, is 15 times stronger than acrylic, and does not corrode.
Dental D is also used to make archless microprostheses. They replace 1-2 teeth, held in place by clasps.
Combined denture
Often bracket dentures, including Quadrotti, are referred to as palatal-less dentures. Their lintel is narrow, but it is still there. A combination denture, on the other hand, really doesn’t have a palate. It’s a gift for patients who can’t tolerate lintel restorations. For example, in case of increased gag reflex, metal allergy, abnormal palate structure. Combined prosthesis will help with epilepsy or increased dryness. It can be fitted in case of bruxism or increased salivation. Durable dentures are placed on the supporting teeth like a mouth guard. The only limitation is that the structure is placed on molars and premolars (chewing teeth). It is important that they are preserved. Such restorations are not cheap and are not available in all clinics. But they have a lot of advantages: food does not get under the structure, the soft backing prevents rubbing, aesthetically they look like real teeth.
Fixed dentures
Restorations that cannot be removed without causing damage are called fixed restorations. They are usually placed on retained teeth or on implants. Fixed dentures are of several types.
Crowns
A crown is a cap made of metal-ceramic, zirconium dioxide, or ceramic that restores a tooth with the root intact. Even if the crown portion of the tooth is severely destroyed, it can be restored by hiding it under a crown. It will take over all the functions of the tooth: biting, chewing. Modern types of dental materials make crowns indistinguishable from natural teeth. This is why metal crowns are becoming a thing of the past – they are too conspicuous. Ceramic crowns allow light to pass through and completely mimic tooth enamel. Metal-ceramic loses out aesthetically. Metal edging in the place of connection with the gum is distinguished by a dark stripe. Such products are better to put on molars. Zirconium dioxide is the strongest material for crowns. So much so that it can erase the enamel of an opposing tooth. Therefore, it is best to discuss the choice of material with your doctor.
Bridges
A bridge is most often used to restore 1-2 teeth. It is 2 crowns on the supporting teeth and artificial teeth between them. The teeth under the crowns are ground down and, most often, depulped. As a result, the tooth is no longer nourished, becomes brittle, and its life span is shortened. But bridges have advantages:
- short fabrication time;
- high aesthetic effect;
- stabilization of dental units.
Bridges are convenient prosthetic teeth, which can be made from a variety of materials. Metal, including precious metal, metal-ceramics, ceramics, zirconium dioxide are suitable for them.
Bridges have contraindications. Dentures are not recommended in case of neglected periodontitis, severely pronounced bite abnormalities, the absence of 3 consecutive teeth.
Prosthetics on implants
In case of complete or partial absence of teeth, it is better to place dentures on implants:
- Implants prevent bone loss. The topography of the oral cavity does not change and the smile remains youthful.
- The lifespan of implant restorations is up to 20 years.
- The prostheses function like natural teeth and do not differ from them in appearance.
- This method makes it possible to use removable and fixed prosthetics and to choose the type of construction for a specific case.
Example of ROOTT implant prosthetics
Implants can restore:
- single defects;
- multiple defects;
- complete absence of teeth.
The main disadvantage of implantation is the high cost. However, in the long run, the investment justifies itself. Implants are installed permanently, and orthopedic constructions have to be changed much less often than in any other method. Implantation has contraindications, but their list is shrinking every year.
Materials for prosthetics
Comfortable and good dentures are obtained from quality materials. Patients have the opportunity to choose, but the doctor’s opinion is decisive. He takes into account many factors, considers the clinical picture, realizes which dentures are more comfortable in this case.
Dental materials for removable dentures
- Acrylic. The most common material in modern prosthetics. It is chosen for its low cost and ease of processing. It holds its shape well, distributes the load. In the manufacture of prostheses made of acrylic, monomer is released, which can cause allergies. In addition, such restorations are prone to shrinkage. Over time, they are covered with microcracks, in which bacteria accumulate.
- Nylon. Elastic and lightweight material, which makes it easier to get used to the restoration. Because a nylon denture is springy, the chewing load is not evenly distributed. Nylon construction does not shrink, but if it breaks, it cannot be repaired.
- Acry Free. More rigid than nylon, but just as lightweight. Hypoallergenic, resistant to aggressive environments. Retains its original appearance for a long time.
- Dental D is a polymer for Quadrotty dentures. It is lightweight but holds its shape well. In terms of stiffness, it is stronger than acrylic, but does not cause allergic reactions.
- Metals. For the metal parts of bracket constructions use alloys of precious metals (platinum, gold), an alloy of cobalt and chromium and medical titanium.
Dental materials for fixed prostheses
- Metal-ceramics. For crowns and bridges, a metal framework is used, on which a ceramic lining is applied. Most often used alloys of chromium and cobalt, although the metal can be different: from iron to platinum. Steel, nickel are also used.
- Ceramics. Brittle porcelain has given way to new alloys. They are very hard, withstand heavy loads, but it is impossible to distinguish them from natural enamel. These are alloys Empress, E-max, Ceramage and others.
- Zirconium. Today it is the hardest material for prosthetics. Processing of teeth under zirconium crowns is the most minimal, because the walls of such a crown are very thin. The construction can be made of zirconium completely, or only the framework, which is then covered with ceramics.
- Ceramic composites. Ceramics in such restorations provide a natural look, while composites provide durability. They are used mainly in implant-based prosthetics. This material allows a permanent denture to be placed immediately after implantation, e.g. with the Resmile technique.
- Metal plastic. The metal framework is lined with a special, wear-resistant plastic. It is used in temporary implant dentures. The design is able to withstand the load and maintain aesthetic appearance for up to 3 years.
What are the differences between dentures
Purpose, method of attachment, material, individual features – everything is taken into account by the prosthodontist before choosing a prosthesis. For the patient, it is important to know the main factors that distinguish one prosthetic method from another.
Product | Restoration of the tooth row | Bone atrophy | Restoration of masticatory load |
Plate | Full or partial | Overgrowth | 60-70% |
Clip-on | Partial | Increasing, but at a slower rate | 70-80% |
Crowns | Individual units | Does not occur | 100% |
Bridge | No more than 2 adjacent units | Does not occur under crowns only | 70-80% |
Implant prosthetics | Any number | Stops | 100% |
Choosing a design is an important task, because the prosthesis is fitted for several years, or even for life if implants are involved. The type of construction determines the service life, the time of habituation and the quality of life. A highly qualified orthopedist is always up to date with new methods and materials, and selects a prosthesis that meets functional and aesthetic requirements and solves clinical problems.