Gingival fistula is a pathological condition, the result of purulent inflammation near the root of the tooth with perforation of the gum tissue. This is a channel in the thickness of the gum, through which pus comes out from the focus of inflammation.
Diagnose and treat the disease by dentists: therapist, surgeon, sometimes a surgeon of maxillofacial specialization.
What is a fistula, how it looks, symptoms
Externally, the fistula is a convex formation with a noticeable spot of white color on it. This means that the pathological process is accompanied by the formation of pus in large quantities.
The fistula is of two types:
- External, when the gingival fistula comes to the surface;
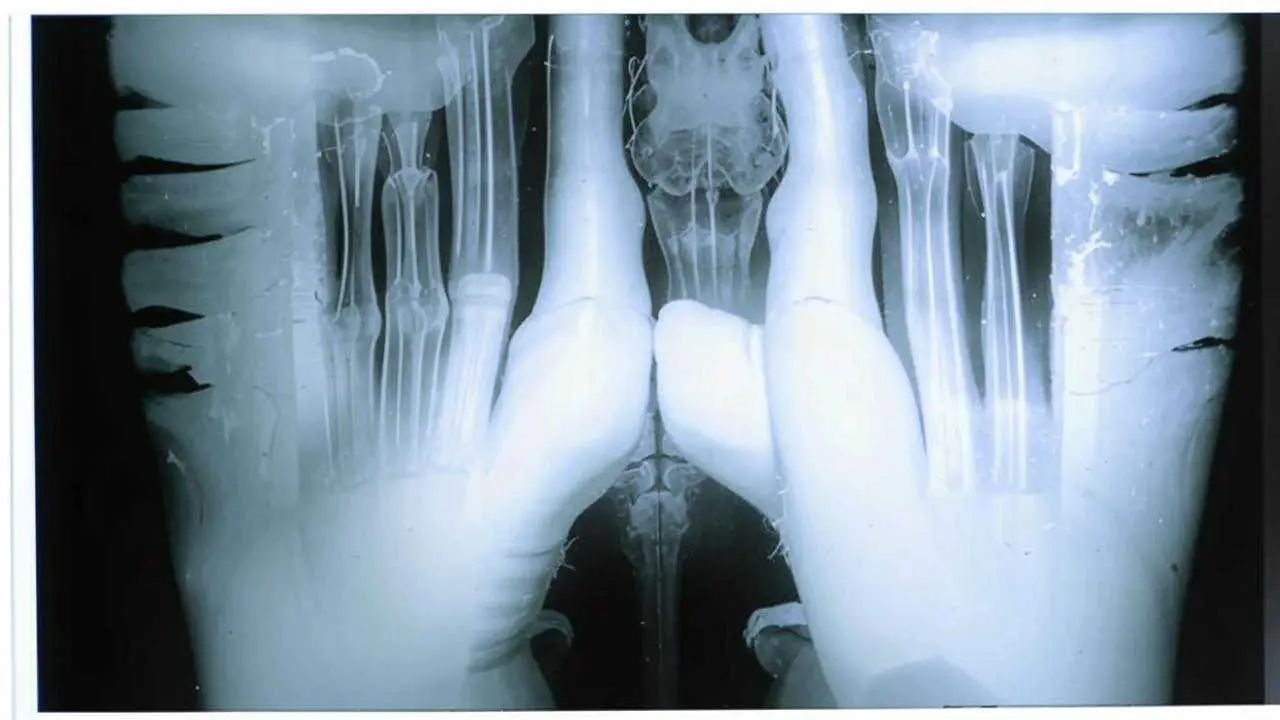
- Internal, when the process remains hidden inside the gum, due to the fact that the fistula channel does not reach its surface. The inflammatory process can only be detected by radiologic examination.
Symptoms of a dental fistula are detected, first of all, during visual inspection. A bulge on the gum is noticeable, from where pus comes to the surface. There are other signs:
- Pain is cutting, stabbing, spasmodic. Becomes worse on exposure (e.g., chewing), eases slightly after some of the purulent contents come to the surface;
- Putrid odor;
- Foreign flavors in the mouth;
- Mobility of the tooth with pathology;
- Swelling of the gum in the area of inflammation;
- Emission of mucus with pus;
- Fever, symptoms of intoxication of the body;
- Inflammation of lymph nodes.
Causes of fistula on the gum in an adult
Fistula is formed due to an infectious purulent process in the dental canal. Pathology can occur for the following reasons:
- Deep caries and its untimely treatment;
- Newly arisen periodontitis and periostitis with the formation of pus;
- Chronic periodontitis, damage to the root walls of the tooth;
- Cystic formations;
- Oncology;
- Pulpitis, damage to the tooth root;
- Granuloma.
Fistula after tooth extraction also occurs. This is a frequent pathology that occurs as a result of infection in the wound.
Fistula after tooth treatment can be formed, for example, when infection occurs as a result of errors in the treatment of tooth decay. Improper filling of a tooth can also lead to the development of pathology. Fistula of the tooth root in this case is formed when pus, having passed through the dental canal, bursts into the surrounding tissues. Most often there is a fistula of the upper and front tooth.
Alcohol, smoking, stress, exacerbations of chronic diseases, carbohydrate abuse, nutritional deficiencies, chronic diseases – all these factors increase the root causes of the disease.
What is the danger of fistula. Consequences
In itself, the fistula is not dangerous, since through it pus is withdrawn from the focus of infection, respectively, the degree of tissue damage is reduced. But the presence of a fistula indicates that the process is serious, and there may be complications of various kinds, such as:
- Loss of teeth in the area of the lesion;
- Accession of secondary infection – inflammation of lymph nodes, ears;
- Sinusitis;
- Gaymoritis;
- Bone tissue damage;
- Sepsis as a result of infection in the general blood system;
- Appearance of cystic formations at the roots of the tooth;
- Complications of the heart, bacterial endocarditis.
Sometimes it happens that the pus comes off almost completely, the fistula heals, and the patient thinks that everything has passed. But in fact, the source of inflammation is not eliminated, so a relapse of the disease is inevitable. Repeated abscesses and fistulas are more difficult to treat.
Diagnosticul
First of all, it is a visual inspection. External fistula is visible to the naked eye. If, however, the fistula in the jaw is hidden, an X-ray is taken. With the help of X-ray examination, the focus of inflammation is accurately identified, the depth of the pathological process of damage to the periosteum. It is important to distinguish the fistula from gingival fatty lesions, purulent inflammation of tissues and other pathologies.
Self-treatment of such a disease at home and self-diagnosis are inadmissible. Treatment is under the control of a doctor, which he prescribes according to the results of diagnosis.
Treatment of fistula on the gum
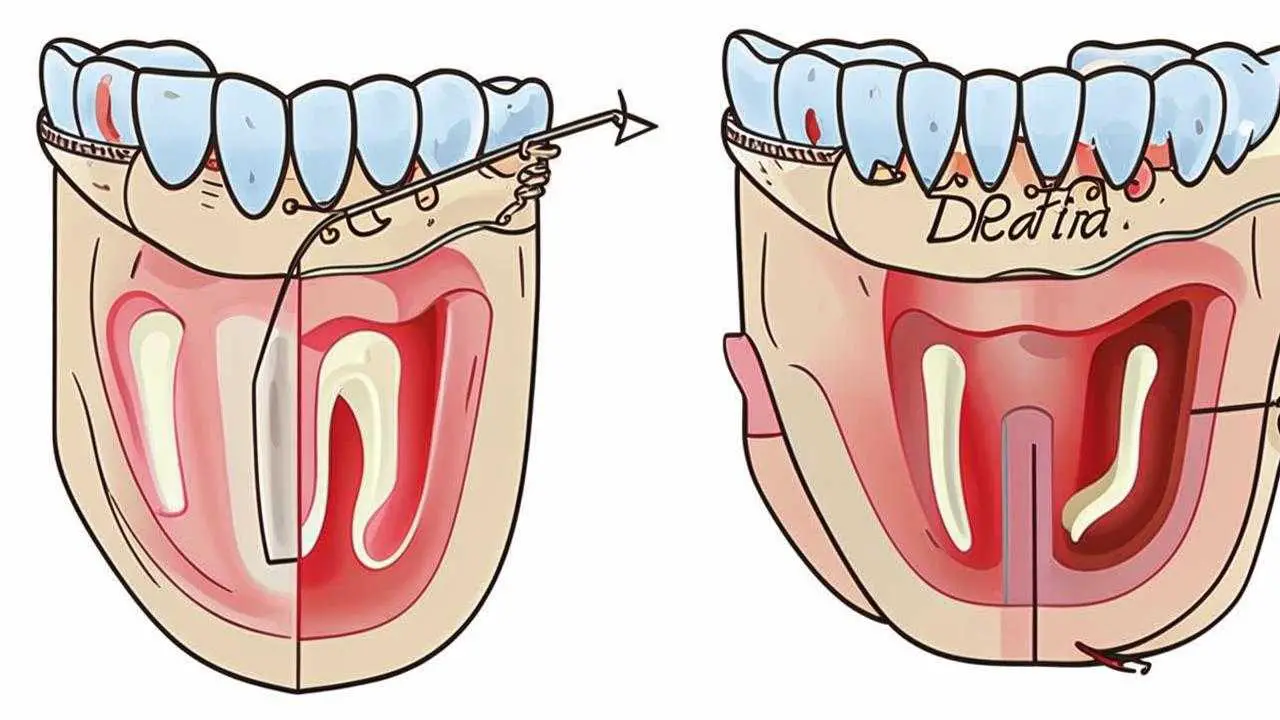
There are several ways of treating a tooth fistula: surgical intervention (the most common) and methods of treating a tooth fistula without removing the tooth. With surgical removal of the fistula on the gum, the inflammatory cavity is opened, cleaned of pus, then a drain is installed to ensure the outflow of purulent contents. Surgical treatment is definitely indicated for a large area of lesions, when the fistula occurs over a tooth covered with a crown, damage to the periosteum.
In the medical treatment of fistula on the gum, conservative methods are used.
These may include:
- Endodontic therapy (preparation of teeth; cleaning of canals, elimination of inflammation, filling);
- Drug therapy (applied at all stages of work on the elimination of pathology), involves taking antibiotics, NSAIDs, antihistamines;
- Physiotherapy. It is never prescribed separately, only in a complex. Increases the effectiveness of any methods of treatment.
Prevenire
To prevent the formation of fistula in the oral cavity, it is necessary to apply preventive measures, namely:
- Professional examinations at the dentist should be done at least once every six months;
- At the slightest suspicion of the formation of a fistula in the area of the upper tooth, front tooth or any other immediately make an appointment with the doctor and follow his recommendations;
- Observe oral hygiene;
- Lead a healthy lifestyle, eliminate bad habits such as alcohol or smoking;
- Eat a healthy diet;
- Reduce coffee consumption;
- Control chronic diseases, avoid their exacerbation;
- Once every six months to undergo a procedure of professional oral hygiene.
Many people ask the question: can you cure fistula on your own, without going to a doctor? The answer is unambiguous – no. It is necessary to eliminate the cause of the disease, not its symptoms. Only a doctor can do this, either surgically or medically. Self-treatment is fraught with the development of complications, increasing the area of pathology, the transition of the process into a chronic state.
Fistula on the gum does not go away by itself. When it is detected, you can not delay with a visit to the dentist, the sooner the root cause of inflammation will be eliminated, the faster the recovery will come. Do not allow the process to develop, in this case the treatment will become longer, more expensive and painful.