The position of the teeth when the jaws are locked together is known in dentistry as the bite. Unfortunately, not everyone has perfectly straight teeth. Most people have bite irregularities. Most often, they are small and few people notice them, but there are situations when the wrong bite is pronounced and causes a lot of inconvenience. In these cases, it is customary to install braces. But what if for some reason it is impossible to install braces? Dentistry has developed methods of correcting the bite with prosthetics, but doctors warn that it is possible to apply them in specific clinical cases, strictly according to indications.
Types of bite
All infants are born with an incorrect bite. Their lower jaw is moved backwards. Through active sucking, it gradually moves forward. When artificial feeding, it is necessary to take this moment into account and do not give children a pacifier with a large opening, so that they train the muscles, ensuring their load.
By the age of 14, a permanent (adult) bite is formed, all milk teeth are replaced by permanent teeth, the number of teeth reaches the physiological norm (28-32).
By this time it is clear what type of bite has been formed:
It is also called a physiologic bite. A normal bite has variants: the lower teeth slightly overlap the upper teeth, the teeth clash, but do not overlap each other, some may be tilted forward. The main definition is that all teeth overlap, there is contact between them, the side teeth overlap without gaps.
The upper teeth cover the lower teeth by more than a third. The contact is broken. Such pathology is called traumatic, because it leads to trauma to the mucosa, erosion of teeth, violation of the temporomandibular joint.
A gap is left between the teeth, as a result, food is not chewed completely. Affects the defect on the process of swallowing and even breathing. The mucous membranes dry up, saliva does not wash away plaque in time, hence the frequent caries, other oral diseases.
The slit is formed as a result of the fact that the upper jaw is strongly extended forward. It is accompanied by violations of the functions of breathing, swallowing, chewing. Often there are painful sensations in the joints.
With this defect, the lower jaw is pushed forward. In this pathology, two extremes can be observed: crowding of teeth or gaps between teeth (tremors and diastemas). With crowding, tartar accumulates very quickly and if it is not cleaned in time, periodontal disease (gingivitis, periodontitis) occurs.
Teeth overlap each other. This defect is difficult to treat, forcing resort to surgical methods. Leads to facial deformation, TMJ disorder, permanent trauma to the mucosa.
Prosthetics in malocclusion
Before starting treatment, the dentist determines the type of bite. This is not always possible only during an examination. The denture bite is determined with the help of radiologic examination, functional and biometric tests.
There are defects that can be corrected only by orthopedic methods, but most often, preliminary orthodontic treatment is necessary.
Indications for orthopedic treatment
- Anomalies of the cranial skeleton in case of refusal of surgical intervention;
- combination of anomalies with a large dental deficit;
- refusal of orthodontic treatment;
- insignificant effect of orthodontic manipulations;
- impossibility to use orthodontic products.
With significant defects, orthodontic and orthopedic intervention is used in combination, prosthetics alone will not lead to progress.
Prosthetics in a deep bite
The task of the orthopedist in this case is to eliminate damage to the mucous membranes, to recreate the occlusion (touching of the teeth when clamping), to distribute the chewing load evenly and to restore the height of the lower face.
To do this, the occlusal surfaces of the teeth are equalized by grinding away the hard tissue. If a large number of units are missing, partial removable dentures with occlusal onlays are used. If the teeth are intact, the bite is corrected with crowns.
Methods of correcting an open bite
Teeth that prevent the jaw from closing are ground down. After a small amount of grinding, the surface is polished and calcium and fluoride preparations are applied for remineralization. If the grinding is of considerable thickness, the tooth is covered with a crown.
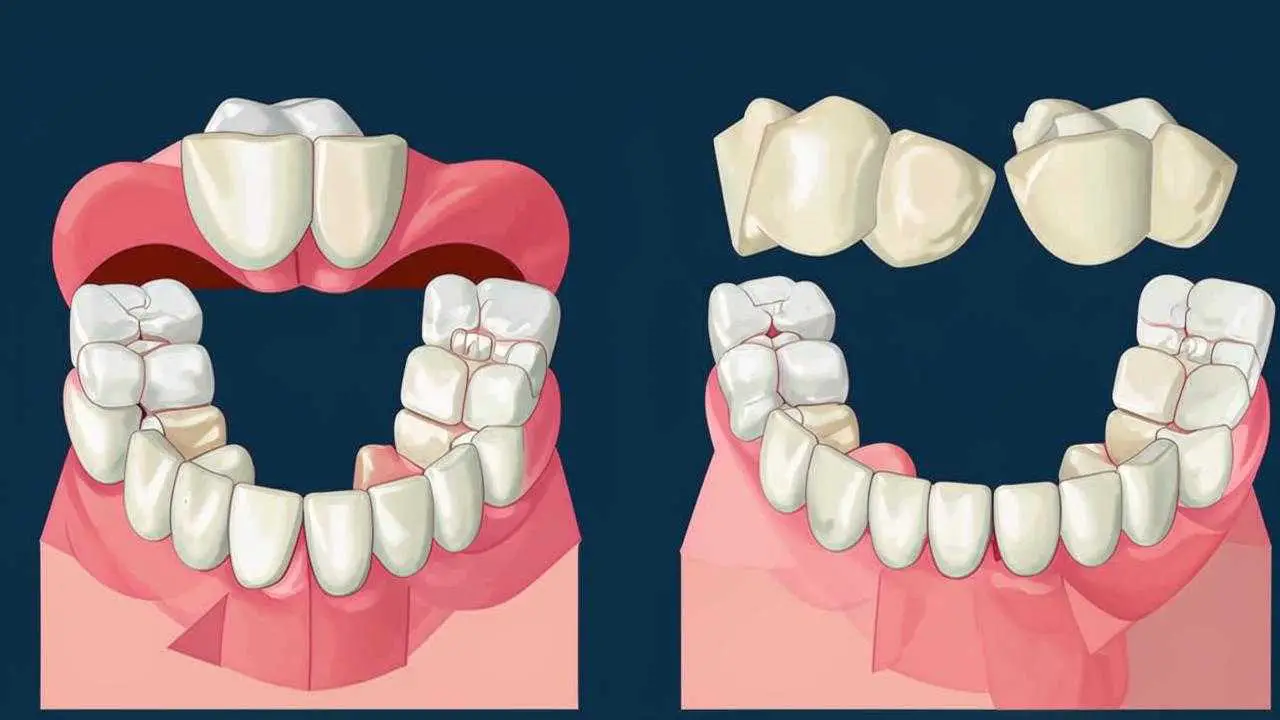
Teeth that lack height are augmented with crowns. In cases of insufficient height of the front teeth, veneers can be used. If all teeth are intact, the main goal is to create occlusal contact. If a part is missing, the task becomes more complicated. It is necessary to restore the tooth row and occlusion at the same time. For this purpose, bridges and removable dentures (brackets) are used.
Dentures for crossbites
Intervention is possible only in the skeletal form of the anomaly, if the patient refused other types of assistance. In a preserved dentition, crowns are placed on the lateral teeth. If there is a large overlap, the natural crown (the part of the tooth that is visible) is shortened by sawing off the excess. If there is a lack of teeth, bridges are used.
In case of minor inclination of the teeth, preparation is limited. With large deviations, inlays are used, changing their axis in relation to the root axis. Such prostheses in malocclusion are used if the deviation does not exceed 15 degrees. A crown is placed on top of the residual limb with an inlay.
Minor defects
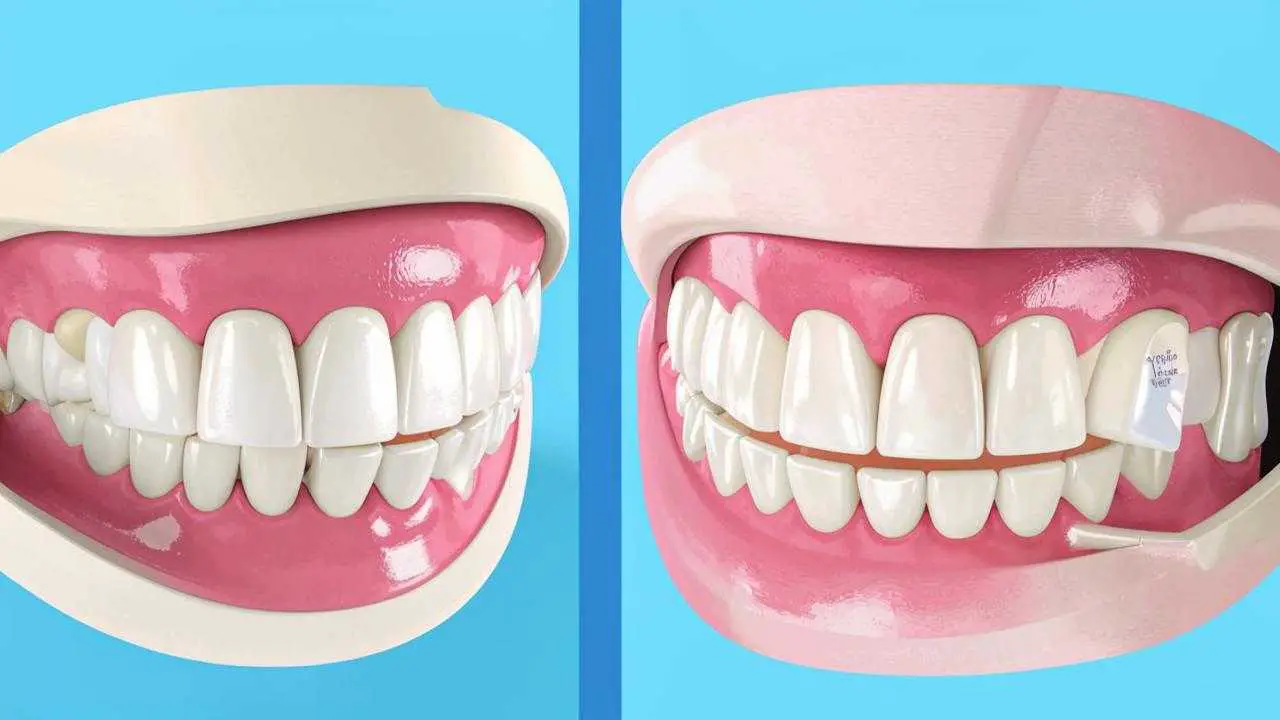
With anomalies in the size and shape of the front teeth, the position can be corrected without the intervention of an orthodontist. Veneers and crowns change the shape, close diastemas (gaps between the front teeth), trems (gaps between other teeth), visually increase the size of the teeth. Increasing the bite height has a positive effect: the lower jaw, which has moved backwards, returns, which reduces the load on the temporomandibular joint. Pain and clicking disappear. Facial proportions are restored and posture is corrected.
Implantation
It is not without reason that dentists insist that if a tooth is lost, it should be restored as soon as possible. Nature does not tolerate a void, neighboring teeth lean toward the gap, and antagonists elongate, protruding from the gum. This makes implantation more difficult.
Surgery is only possible if the neighboring teeth do not interfere with the implant. However, if the roots have shifted or the crowns are severely tilted, orthodontic treatment must be performed first.
In case of jaw defects, everything depends on their severity. In case of small irregularities, it is possible to correct the bite with the help of prosthetic teeth after implantation. In case of severe abnormalities, it will not be possible to achieve a positive result.
There is a method of orthodontic prosthetics, in which braces are fixed on micro-implants. The fixed support is better able to bear the stresses than living teeth. Once the orthodontic prosthetics are complete, the micro-implants are removed.
Prosthetics for malocclusion require special skill and thoughtfulness. If the dentist believes that without orthodontic treatment can not do without, it is worth listening to him. The price for complex treatment is higher, but the result is of higher quality. Although some defects can be corrected by orthopedic methods, the greatest effect is achieved as a result of a comprehensive approach (orthodontics and prosthetics).