Sooner or later we all have to use the services of a prosthodontist. A crown on a decayed tooth, a bridge, a bracket or plate prosthesis, veneers – whatever method we use, the success of treatment depends largely on the preparation for prosthetics.
Specific measures may vary depending on the type of work, but there are general principles. If they are not followed, it may be a reason to change dentistry. A qualified prosthodontist is interested in the result of his labor. Such a doctor understands that there are no trifles.
Psychological preparation
Most people are afraid of going to the dentist. A patient who is stiff, shaking from fear does not go well to a conversation, it is difficult to interact with him. The work of the prosthodontist begins long before the fitting of the prosthesis. The first thing to do is to establish emotional contact. If the doctor is friendly and attentive, he is trustworthy. The patient will be more open to discussing treatment methods, nervousness will decrease. During the conversation, the dentist collects information about:
- the patient’s complaints;
- past treatment experience and results;
- the presence of common diseases and allergic reactions.
During the examination, the prosthodontist pays attention not only to the condition of the oral cavity, but also to facial asymmetry, cheek and lip depression.
To assess the condition of the teeth and see hidden defects, an orthopantomogram (panoramic image) or CT scan is usually ordered. This is not a whim of the doctor, but a desire to create a complete picture, taking into account all the details. In addition, the image can reveal inflammatory processes that are not visible during the examination.
Based on the results, different types of preliminary treatment are prescribed.
Therapeutic phase
In preparation of the teeth for dentures, a complete oral sanitation is performed:
- treatment of caries, pulpitis, periodontitis;
- elimination of inflammatory processes in the periodontium;
- removal of tartar, plaque;
- polishing and grinding of enamel;
- depulping (nerve removal).
Not all procedures on the list are mandatory. The patient may have healthy or well-treated teeth, but plaque removal is necessary. This reduces the risk of infection.
Removing the pulp is now widely debated in the dental community. Most agree that each case deserves separate consideration, but still practice shows that it is safer to depulp the tooth.
This is due to the fact that there is a risk of inflammation under the crown, in which the entire structure is removed.
Removal of the pulp is mandatory if:
- it is planned to remove a thick layer of hard shell, leaving the dentin exposed;
- in case of a significant inclination, which is corrected by turning;
- when splinting the teeth of patients with periodontitis.
Preparation of gums for prosthetics, includes the management of inflammatory processes, treatment of periodontitis, stomatitis, healing of the wells of extracted teeth (except in cases of transgingival implantation).
In some cases, therapeutic procedures are not enough, then additional manipulations are carried out.
Surgical stage
Some teeth have to be extracted before prosthetic intervention. This is done if:
- the therapeutic treatment has had no effect;
- the pulp of the tooth is inflamed and this condition is chronic;
- the teeth are retined (not erupted) or dystopian (misaligned);
- the root of a tooth is fractured;
- orthodontic indications.
Bone growths – osteophytes and exostoses – are also removed. The layer of mucosa covering them is very thin, the denture can easily injure it and rub it, causing pain and discomfort. Therefore, they are removed by leveling the gum margin.
What exostosis looks like
To prepare the oral cavity, remove excess mucosa, scars, palatine roll – everything that can interfere with prosthetics.
The surgical preparation of the oral cavity for prosthetics also includes:
- implantation;
- bone grafting;
- sinus elevator.
Orthodontic stage
Treatment is aimed at correcting bite and occlusal defects (contact between the teeth of the upper and lower jaw). Teeth are moved with the help of brackets, mouth guards and plates. This is done not only to correct the bite, but also to correct the position of the supporting teeth and to form a place for fixing dentures.
Orthopedic stage
Only after all the preliminary procedures, the orthopedist begins the final stage of preparing the oral cavity for prosthetics.
At this stage, the work depends on the specific type of prosthetic construction.
Preparation for removable prosthetics
After the preparatory work, the orthopedist determines the type of product, the method of fixation, the supporting teeth.
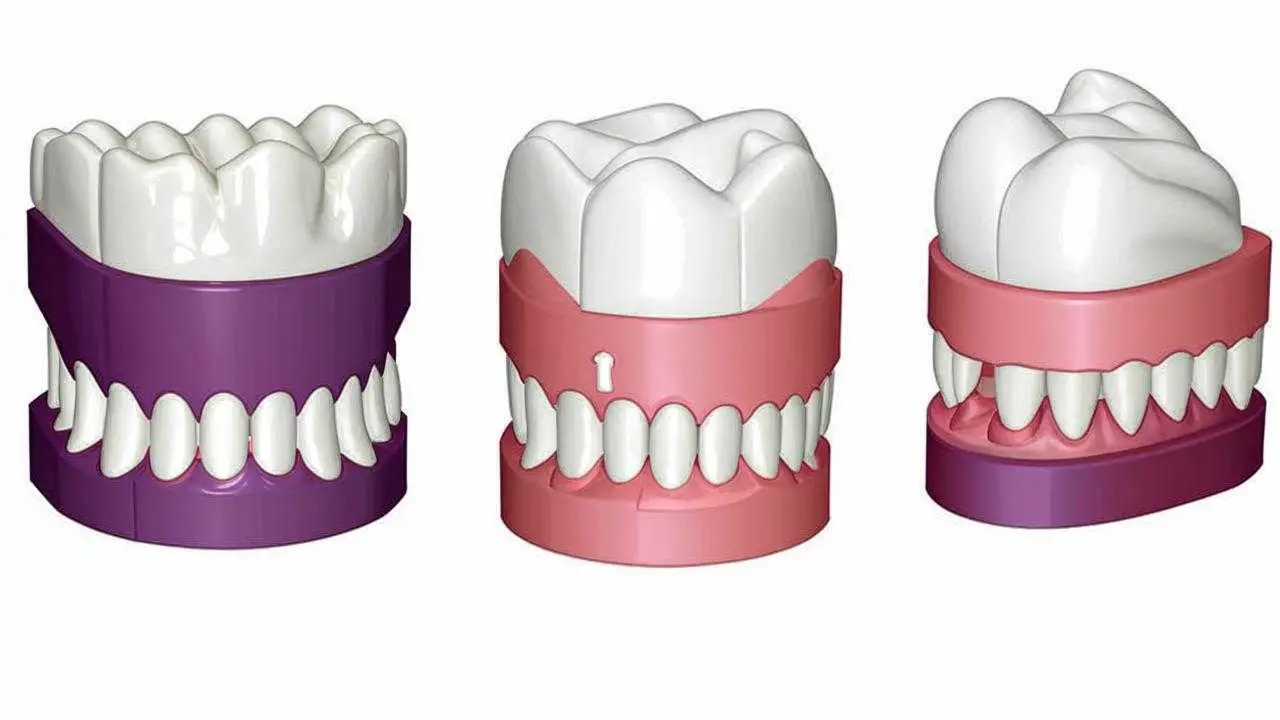
These can be:
- Full removable prostheses. Plate products are made of acrylic, nylon or new polymers such as AcryFree
- Partial removable dentures. They can be plate, bracket, adhesive, or immediat (temporary).
The doctor makes impressions of teeth, on which the laboratory makes plaster or wax models, on the basis of which the prosthesis is made. In the case of bracket prosthetics, a metal arch made of selected materials is cast – a bracket, and the base and crowns are placed on it. The orthopedist performs fitting and correction, after which the patient is given time to get used to it. After another correction is possible and the rehabilitation period begins. Its duration is different for each patient.
Crowns
Crowns are placed
- on teeth that have been depulped to prevent them from decaying;
- On units that are more than 50% decayed;
- teeth in which only the root is preserved;
- abnormal abrasion of enamel;
- for aesthetic defects that cannot be corrected by other means;
- on implants.
After all preparatory manipulations, the doctor trims the tooth to the thickness of the future crown. If the tooth is completely destroyed, a post is inserted into the root. Then the preparation of the stump of the tooth is carried out. It is given a shape that will allow you to put the crown on top and ensure its stability.
After that, impressions are taken of the teeth, necessarily of both jaws to ensure good occlusion (touching) of the teeth. Based on the impressions, the laboratory will fabricate the crowns, which the doctor will fit so that they fit snugly on the supporting tooth.
During the fitting, the prosthodontist checks the correctness of the bite, contact with neighboring teeth, and how comfortable the patient is with the crown. For the first few days, it is recommended to wear the crown on temporary cement to get used to it. Then, if necessary, another fitting is carried out and the crown is fixed on permanent cement.
When placing a crown on an implant, both cement and screw fixation are used.
Bridge
The main preparation for a bridge is the preparation of the supporting teeth. When metal-ceramic dentures are used, the teeth are subjected to significant grinding. Zirconia crowns are much thinner, so not as much hard tissue is ground down.
After that, impressions are made and the framework is modeled after them. The crowns are then cast and fired in a kiln. The bridge is tried on, adjusted and placed on temporary cement, giving the patient time to get used to it. After that, the structure is cemented with permanent cement.
Veneers
Preparation of the jaw before prosthetics consists in the sanation of the oral cavity, taking impressions, making a 3D model. According to this model, individual onlays are made, which the doctor fixes to the pre-prepared teeth.
Prosthetics on implants
Preparatory work includes all the necessary procedures. After that, in a two-stage protocol, wait until the implants take root, then make impressions and make dentures according to the general scheme.
In the one-step protocol, the temporary is placed immediately after implantation. After about a year, permanent dentures are made and fitted. Prices for implant prosthetics may be higher, but the structures last longer and are more reliable, making the cost not as high as it may seem at first glance.
The ROOTT ICSDI in Moscow provides a full range of preparatory measures for prosthetics. Its own laboratory, therapeutic, surgical, and orthopedic departments guarantee well-coordinated work of doctors and excellent results.