Fluorosis is a chronic pathology of tooth enamel that occurs due to an increased concentration of fluoride in the body. It is manifested by the formation of spots, defects of different size, color, and shape on the enamel. The disease is epidemic in nature. Dental fluorosis is characteristic of areas with excessive fluoride content in drinking water. Also, workers of some industrial enterprises (plants for the production of aluminum, laser equipment, etc.) are susceptible to the disease, due to the increased content of fluoride compounds in the air.
Causes of fluorosis
Fluoride is an element that enters the body with water, vitamin supplements, foods, air. It takes part in the formation of dental and bone tissue, strengthens enamel, prevents the leaching of calcium from the body. However, if the lack of fluoride increases the risk of carious destruction of teeth, the excess leads to the development of dental enamel fluorosis.
Classificatie
According to anthropogenesis, fluorosis is divided into endemic and occupational. Although the clinical manifestations in both types of the disease are similar, the approach to treatment is different. In the professional form of the disease affects not only tooth enamel, but also bone tissue, osteosclerosis and osteoporosis develop. As the disease progresses, disorders of the vascular system, liver, the risk of osteosarcoma increases many times. In this case, fluorosis spots on the enamel layer are often absent.
Forms of fluorosis:
- spotted;
- streaky;
- erosive;
- chalky mottled;
- destructive.
Spotted and streaky fluorosis is a mild type of pathology, erosive and destructive are considered to be severe. A patient can be diagnosed simultaneously with different forms of the disease – on individual dental units, groups of teeth there is a different clinical picture.
Symptomen
Dental fluorosis is characterized by the appearance of pale spots or numerous streaks on the enamel. In the course of the disease, the defects receive a yellow, brownish shade. Defects more often affect the maxillary incisors, against the background of excessive concentration of fluoride compounds, the disease covers all teeth. Increased abrasion of enamel develops, chipping and erosive areas appear on it. Symptomatic manifestations depend on the type of pathology:
- Stirich fluorosis – small stripes (strokes) have appeared on the enamel, at first they are weakly manifested, further united into one large spot, the structure of which is made up of individual strokes.
- Spotted – this form is characterized by the appearance of numerous whitish (chalky) spots, joining together. The spots are characterized by a smooth, surface with a glossy sheen (similar to caries in the spot stage). Unlike a carious defect, they do not have clear boundaries, but smoothly merge with healthy areas of enamel.
- Chalky mottled – pigmented spots with clear boundaries are formed, multiple dots are visible. The enamel layer turns yellow, rapidly thins, dentin is exposed, the tooth becomes very sensitive to mechanical, chemical and thermal stimuli.
- Erosive fluorosis – there are voluminous defects – erosions. Tooth enamel in these areas is completely absent, dentin tissue is exposed.
- Destructive – a severe degree, in which not only enamel, but also dentin is destroyed. The tooth is brittle, subject to chipping, fractures, the crown part is deformed, the defects are very noticeable.
Destructive type is found in an area where the level of fluoride compounds in the water is from 10 mg / l and higher. Pathology can cover several dental units or the entire row.
Diagnostic methods
Diagnosis of dental fluorosis is not difficult. The doctor relies on the clinical picture characteristic of each degree of lesion. Differential diagnosis includes:
- Minor enamel opacities are detected by drying the surface to assess the state of the protective layer in the area with altered pigmentation.
- Vital staining method – in fluorosis the affected areas of enamel are not susceptible to staining with methylene blue, unlike carious defects.
- Luminescence study – mild types of the disease in ultraviolet light weakly glow, with medium and severe forms, there is a partial quenching of fluorescence.
- Micro-radiography – aimed at determining the depth of the lesion of dentin tissue.
It is obligatory to send to the laboratory drinking water for analysis, to determine the percentage of fluoride compounds.
Treatment
Treatment of dental fluorosis is selected taking into account the type of pathology, symptoms, their severity. Preparation of defective areas with subsequent filling is ineffective, since there is a high risk of further destruction of tooth tissue. To strengthen the enamel prescribe calcium- and fluoride-containing drugs.
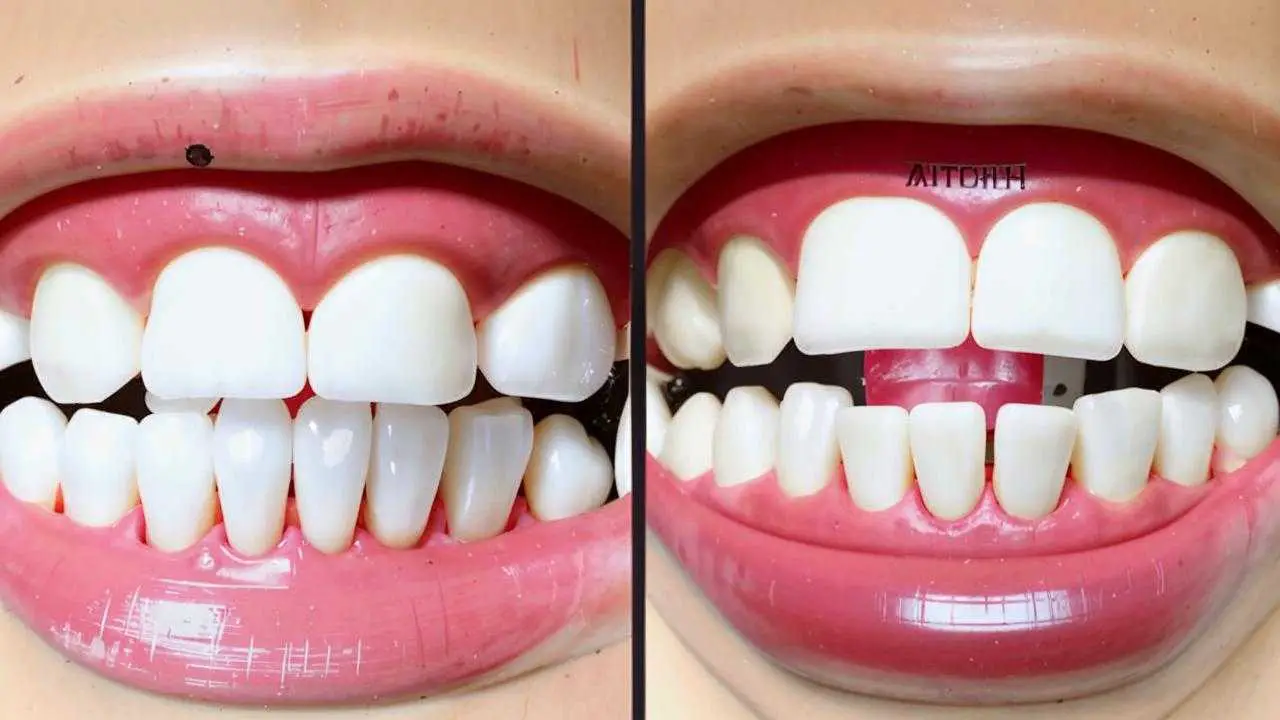
At the initial stages of the disease, a course of teeth whitening with subsequent remineralization of enamel. Chemical, laser, LED methods are used. Whitening in fluorosis is performed by safe means, the basis of which are inorganic acids. The course of treatment involves 10-15 sessions. To consolidate the result of therapy, it is recommended to repeat the course after 8-10 months.
In medium and severe forms of fluorosis qualitative whitening is impossible. Methods of aesthetic restoration are used:
- Installation of veneers, lumineers – thin overlays (plates) made of porcelain, ceramic, zirconium are attached to the outer part of the tooth with a special composition.
- Composite restoration – the doctorrestores the tooth surface layer by layer. Composite materials of different shades and translucency are used. This allows you to choose a natural shade, the restored units will not stand out from the general row.
- Prosthetics with crowns – artificial metal-ceramic, ceramic crowns are fixed on pre-prepared fluorosis teeth (depulped, ground).
Example of restoration of teeth with zirconium dioxide crowns:
Orthopedic treatment is guaranteed to eliminate cosmetic imperfections, as well as prevent further destruction of dental tissues, eliminate hypersensitivity of teeth.
Preventie
With a timely appeal to the dentist, following the doctor’s recommendations, the prognosis is favorable. Even the most severe course of the disease leaves an opportunity to restore the aesthetics of the smile. The earlier the patient comes to the doctor – the easier and more effective the treatment.
Fluorosis prevention measures include control of fluoride levels in drinking water. It is recommended to use filters for additional purification of tap water, purchase bottled water.
Obligatory full, balanced diet. Minimize the consumption of foods rich in fluoride (sea fish, spinach, nuts, seaweed, etc.), eat more dairy products, fruits, vegetables. Refuse fluoride pastes, rinses. Take calcium preparations to strengthen dental tissues. Visit the dentist at least 2 times a year.
In clinics ROOTT in Moscow, successfully treat fluorosis lesions of any form, degree of severity. Dentistry has all the possibilities for safe whitening, effective restoration of teeth.