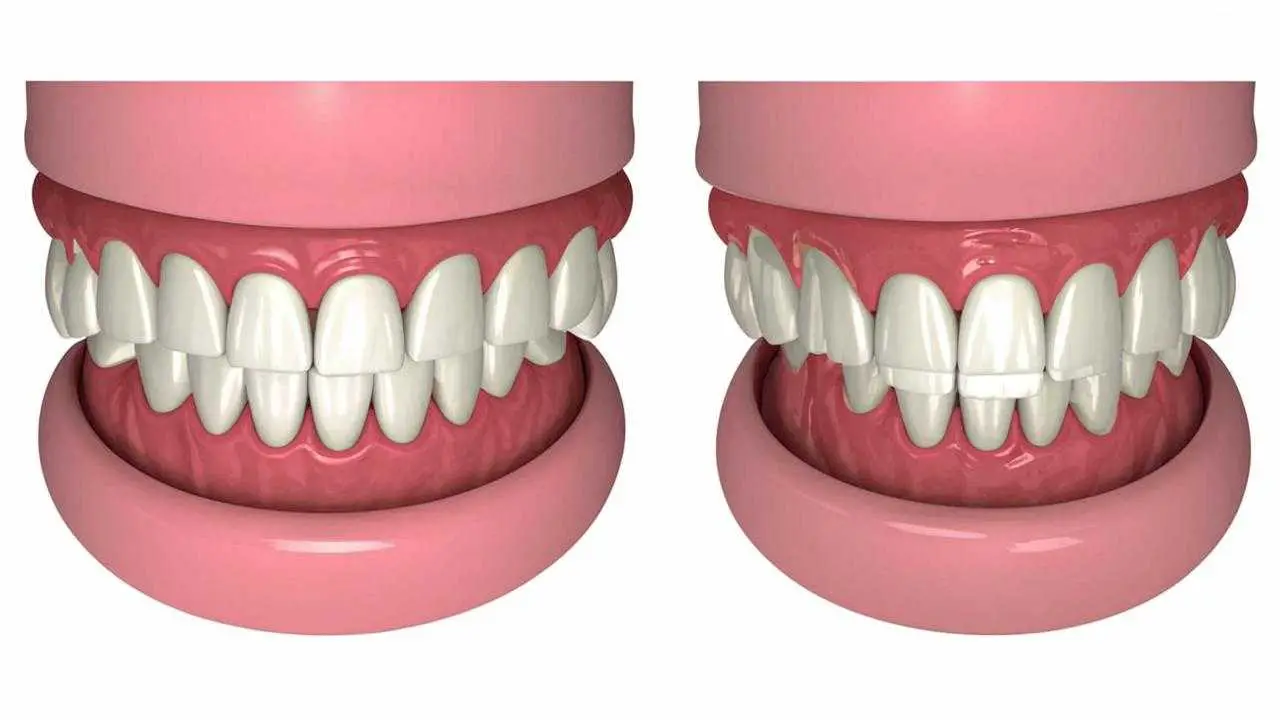
A malocclusion is a misalignment of the lower and upper jaw in relation to each other. Distal overbite is a fairly common type of this anomaly.
What is a distal bite
If the lower jaw does not develop properly, the upper jaw may prevail over it. That is, if the upper jaw strongly protrudes forward, and the lower jaw is underdeveloped, we can talk about a distal (prognathism) bite.
Symptoms
With dental occlusion, the following facial features are characteristic:
- large cheeks and cheekbones, the face appears convex;
- the wings of the nostrils look upwards;
- the profile is called “bird-like” because of the small lower jaw;
- because the lower lip is tucked under the front teeth, the mouth may often be half-open;
- the upper lip is more dense;
- the chin has a pronounced crease.
The patient speaks with whispering or mouthed, the more severe, the greater the degree of distal dentition. Postural abnormalities are characteristic.
For the teeth and jaws, symptoms include:
- a tooth row pointing away from the lower jaw;
- gaps between the antagonist anterior teeth of more than 5 mm;
- crowding of the teeth, some elements are expanded;
- underdeveloped narrow lower jaw;
- the lateral teeth may not close completely.
Pathology can occur in combination with an open, deep bite. If a distal open bite is fixed, it is necessary to start treatment immediately to try to avoid surgery.
Causes of the disease
The causes of distal overbite can be laid in the intrauterine development. When the skull and maxillofacial joints are formed. The disease of the pregnant woman, taking certain drugs and medications can affect the appearance of pathology, as well as other factors:
- heredity;
- rickets, bone diseases;
- poor posture;
- early/late change of baby teeth;
- deviated nasal septum, ENT diseases that make nasal breathing difficult and make it a habit to breathe with open mouth;
- the habit of sucking fingers, chewing on pens, etc.;
- traumas, fractures of teeth;
- incorrectly fitted removable dentures or improper use of them.
Up to 90% of babies have exactly distal bite, the anomaly of the dentition is not always pronounced. In the adult population, such a defect occurs up to 30% of the total number.
Classification
There are several varieties of classification of distal bite.
According to the location of the upper tooth row relative to the lower:
- I form of bite. The incisors are arranged in a fan as the jaw arch narrows in the lateral regions.
- II form. The anterior teeth are inclined to the palate, and the lateral incisors are partially expanded and have a distal slope.
According to the morphological sign distinguish:
- dentoalveolar form. The defect is expressed due to malpositioned teeth, the alveolar processes do not correspond to each other. Lower incisors often traumatize the upper alveolar ridge.
- Gnathic form. Abnormal development of the jaws and their location in the skull.
- combined form. A combination of dental and jaw anomalies.
Another classification of distal occlusion according to Betelman:
- lower micrognathia, and the upper jaw is normal;
- the upper jaw is enlarged and the lower jaw is normal;
- the upper jaw is enlarged and the lower jaw is underdeveloped;
- upper jaw pronation and lateral compression of the dentition.
Complications
The consequences if deep distal dentition is not treated can be as follows:
- GI problems due to impaired chewing, swallowing. All the load goes to the posterior lateral teeth;
- increased abrasion of teeth, as a result of which caries easily occurs, untreated it can go to the granuloma of the root and be the cause of tooth loss;
- ugly facial features, “bird profile”;
- periodontal inflammation, traumatization of gum and palate tissues by cutting edges of teeth;
- impaired diction;
- discomfort, pain in the temporomandibular joint.
There may also be complications with implants and prosthetics.
Diagnosi
To assess the degree of pathology, the choice of method of treatment of distal bite, the possibility of making correction without surgery requires a multifaceted diagnosis, which consists not only in a visual inspection of the doctor, a visit to the orthopedist, but also needs:
- radiography, computed tomography;
- three-dimensional projection of the skull will be very informative;
- casts of teeth.
To track the dynamics of treatment, photos of different angles before and after are necessary.
Methods and stages of treatment
Treatment in children and adults is different. The bones of the jaw at an early age are growing, they and the teeth are easier to put in place, as it is more difficult to correct a distal bite with established tissues.
Methods of correction of distal occlusion in children
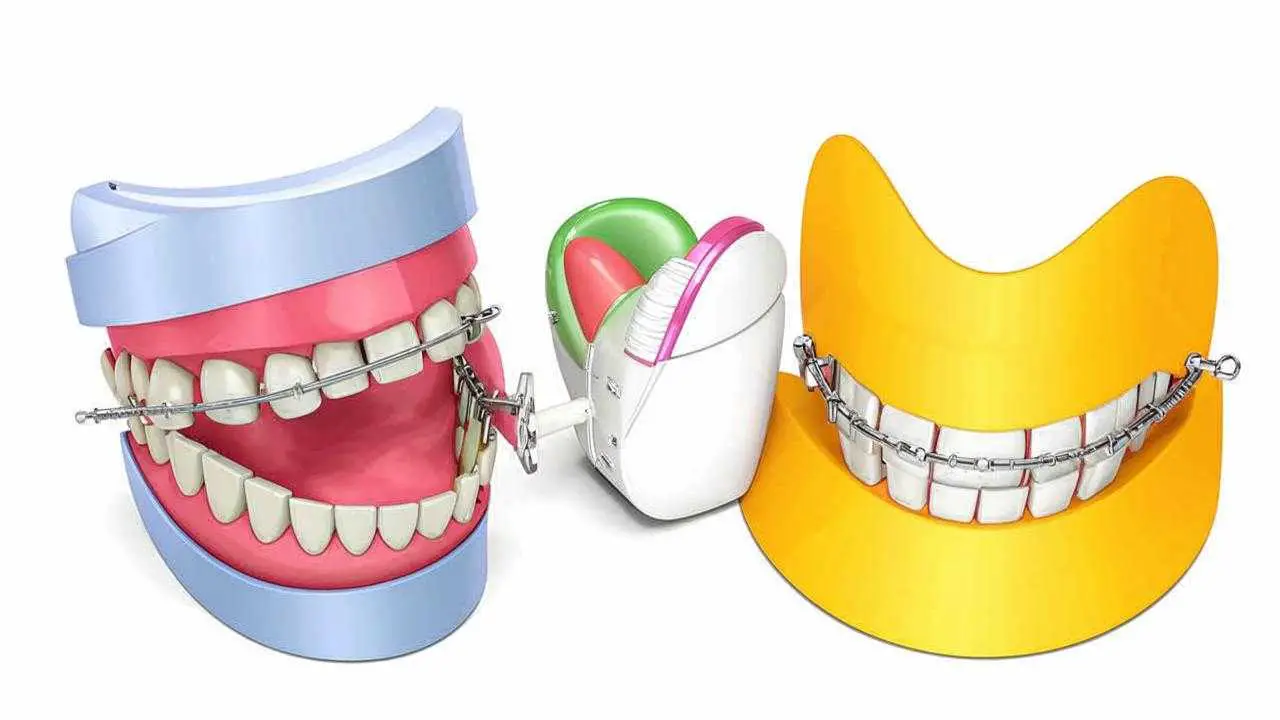
It is possible to start therapy from the age of 3 years. This will be myogymnastics, alveolar massage, later the use of orthodontic appliances. They will help to stimulate the growth of the lower jaw and slow down the upper jaw. These are the Frenkel adjuster, Rogers, Dass activators, models complete with screws, etc.
Trainers – elastic mouth guards, train the muscles, relaxing the tone of the overly tense ones. They are worn at night and used a couple hours a day. May need to be worn for 4-12 months.
Orthodonticplasty with a metal arch applies a certain amount of force to the teeth. The result will be in 6-18 months.
Correction of distal bite with braces can be prescribed as early as adolescence. A bracket system is a fixed structure (external metal, lingual, ceramic). A bracket is fixed on each tooth and a metal arch is threaded through it, by applying pressure to the pathologic area forces it back to the correct position. Within a few years of use(1-2 years), the system will be able to align the teeth and change the bite.
Treatment of distal bite in adults
With a not too severe form of pathology, braces, splints, a chin mouth guard and elastic traction are sufficient. On average, it will take 1.5 to 3 years to correct the distal bite with braces.
Surgical treatment of occlusion may include only extraction of a few teeth, in case of a deep distal bite an operation (osteotomy) will be performed to cut the jaw tissue and install a corrective structure. Its task is to stretch, lengthen the lower jaw with the correct positioning in the TMJ area. After that, it will be necessary to wear braces or other devices for a specified period of time.
Prognosis, timing
The prognosis for the treatment of distal bite is favorable. Up to 95% of patients solve this problem with an orthodontist. And the earlier the correction begins at an early age, the faster and easier it will go. For children it may take six months to a year, and for adults – several years.
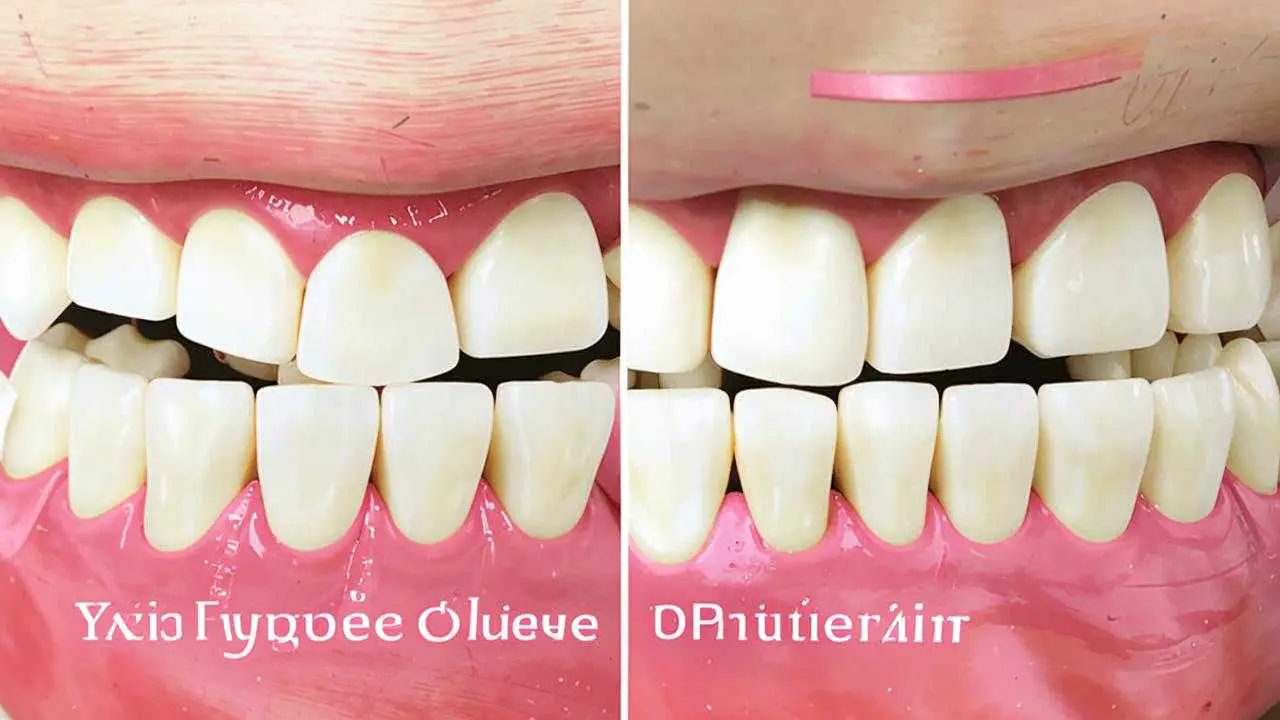
The photo shows an example of correction of distal bite in the ROOTT clinic.
Prevention
To exclude bite pathology, it is necessary to seriously monitor health during pregnancy. The first trimester is the most difficult, during this period the skeleton and the skull of the child are formed, and taking medications, stress can affect the course of this important process.
It is necessary to exclude bad habits of the child: long sucking fingers, fists, etc. Preserve breastfeeding.
Correct posture affects the position of the jaw. Pay attention to how your pupil, student and yourself sit.
Nasal injuries, ENT diseases must be corrected so that mouth breathing does not become a habit.
Since the prognosis is always good, you should not delay in starting treatment.
Clinics in Moscow offer services to change the distal bite. For successful correction, you should choose one where only highly qualified orthopedists work and there is authorizing documentation.