Tempo di lettura ~ 5 min Numero di letture: 13794
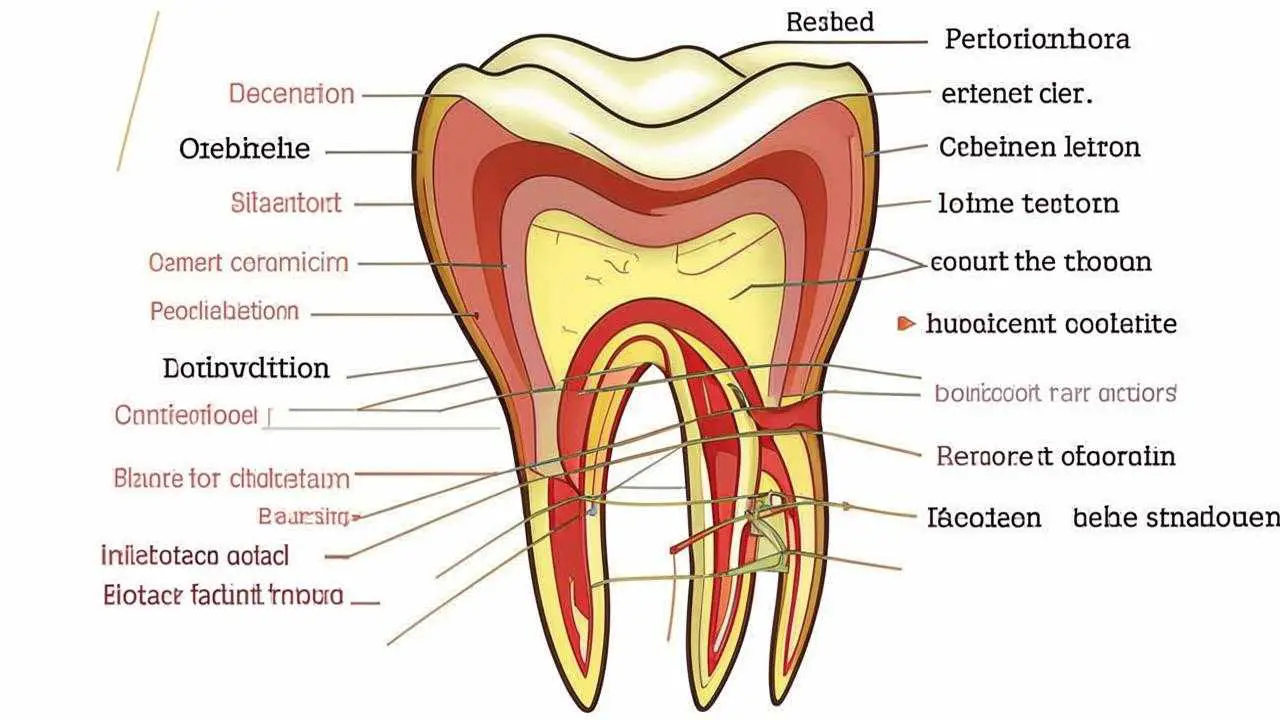
Tooth dislocation – a dental injury in which the incisor or canine due to mechanical impact is displaced in the alveolus (well) in the lateral or vertical position. Due to the peculiarities of the anatomical structure, the upper incisors and canines are more often subjected to such injuries. Anatomically, each dental unit consists of a crown and root. The crown part is located above the gum, the root – in the jawbone (alveolus, hole).
Between the alveolus and the root is the periodontal ligament, consisting of connective tissue fibers. Intertwined with the alveolus and root cementum, the periodontium holds the root in the jaw. The combination of the 3 elements (alveolus, periodontium, cementum) is called the ligamentous apparatus of the tooth. It can be traumatized by impact, biting on a hard product or object, resulting in dislocation or subluxation of the root and its disposition in the tooth row. Traumatic tooth dislocation on the lower jaw is less common than on the upper jaw.
Timely referral to a doctor makes it possible to save a traumatized incisor and avoid extraction. According to the severity of the injury, adequate treatment is carried out, including immobilization of the dental unit by fixing it to adjacent teeth. Even if the incisor has fallen out, but the root and crown are preserved, it is possible to restore the tooth with replantation if it is treated quickly.
Causes of dislocation
- Impact, falling;
- biting, chewing hard food;
- bad habits (breaking bottles with teeth, biting nuts);
- unsuccessful extraction of a neighboring tooth unit;
- hard objects in food.
Symptoms
- Disposition of a tooth unit in the row (from slight mobility, to falling out);
- Severe pain in the area of the lesion;
- impaired chewing, speech functions;
- swelling, redness, increased gingival sensitivity;
- difficulty in closing the jaws.
Dislocation of a deciduous tooth is one of the most common injuries in children under 3 years of age. The most threatening is an embedded tooth dislocation, because in this case the bone floor may be destroyed, which will prevent the formation of a permanent unit. Signs of tooth dislocation in children are similar to the symptomatology in adults.
Classification
- Incomplete dislocation of the tooth – the crown part is displaced in different directions or rotated around the axis, the incisor is mobile, but held in the hole. The tooth unit responds to touch with sharp pain. The gingiva is separated from the hard tissues of the crown, bleeding, reddened, swollen. Such trauma can be complicated by the destruction of the pulp chamber (internal cavity with a neurovascular bundle), atypical changes in the root part (shortening, curvature).
- Complete dislocation of the tooth – the crown part with the root completely fell out of the hole, the gingiva was separated, swollen, turned livid. Where there was an incisor there is a bleeding hole. Such an injury occurs more often with deciduous tooth units, since they do not have a developed root system.
- An embedded toothdislocation implies a shift of the tooth unit to the side of the jaw. The crown part is completely or significantly immersed in the gum tissue (visually – the height of the visible part decreases). Trauma may be accompanied by root splitting, destruction of the jaw bone, damage to the pulp, rupture of blood vessels.
Possible complications
- Formation of granuloma, root cyst;
- Chronic inflammation of the periodontium;
- excessive expansion of the traumatized incisor;
- in children, stoppage of growth and formation of the root of the permanent tooth;
- root resorption;
- pulp necrosis;
- shortening and curvature of the root part.
Diagnosi
Only a dentist can differentiate root dislocation from a fracture. Not only the incisor is damaged, but also the peri-dental tissues. The formation of a fracture in the jawbone is possible. Comprehensive diagnosis includes:
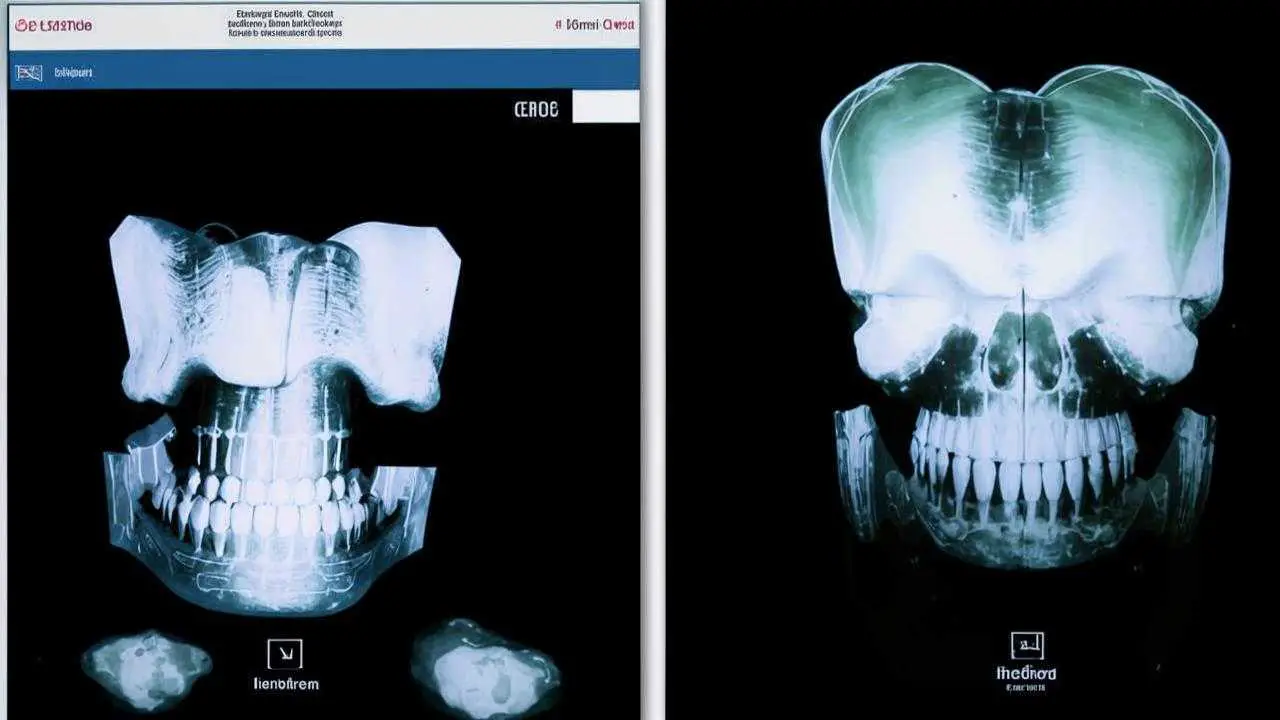
- Orthopantomogram;
- A targeted image of the incisor;
- CT SCAN;
- a three-dimensional scan of the maxillofacial area.
The dentist makes a diagnosis based on examination, complaints, X-ray results. The doctor analyzes the clinical picture, assesses the condition of the jawbone in the injured area.
Treatment and prognosis
How to treat a tooth after dislocation, the doctor determines based on the type of traumatic injury. The decision on the method of treatment is made according to the condition of the jawbone, the degree of displacement detected.
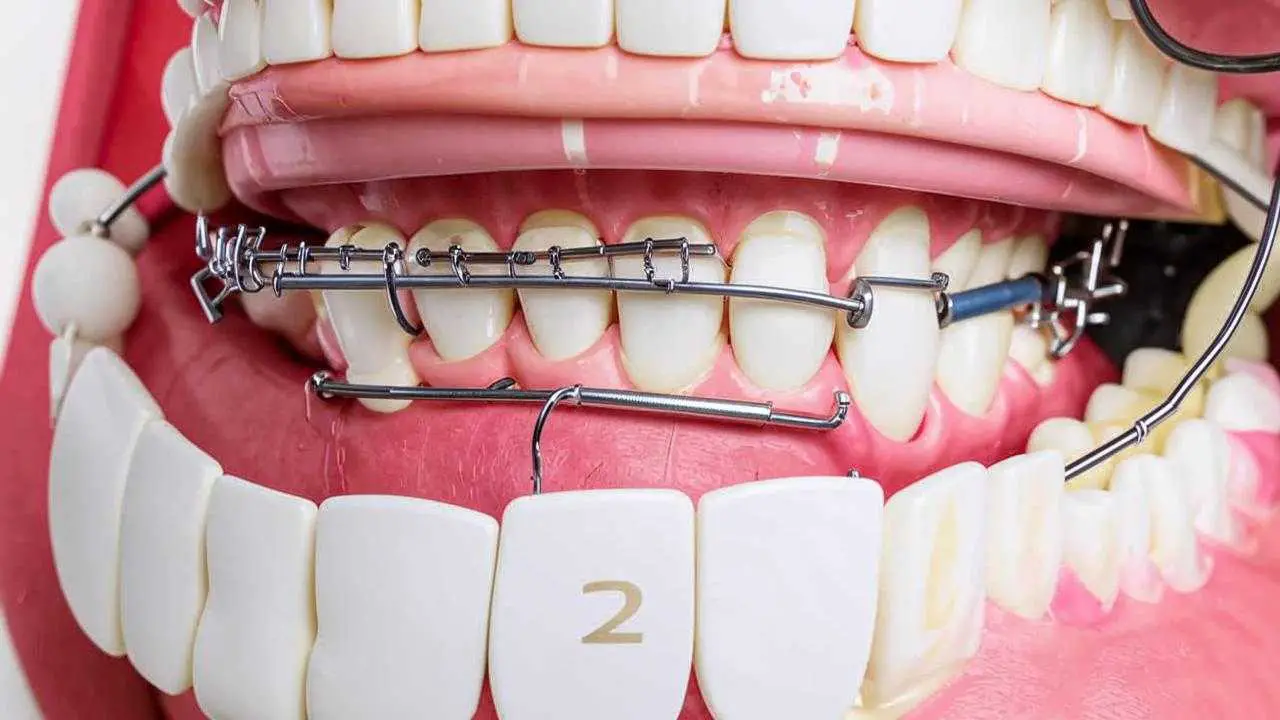
- With a pronounced displacement, the dentist pulls the incisor with special forceps to the former position, fixes it with a splinting device.
- In case of minor toothdisposition, splinting is not always required, the unit is often restored on its own.
Partial dislocation of anterior teeth involves these treatment steps:
- Repositioning (the incisor is returned to its correct position);
- Fixation with a splinting structure (splints, brackets, mouth guards, etc.);
- depulpation and filling of the dental canals (if the pulp has died).
If an injury has occurred, you should seek help from a dentist as soon as possible. Even with a complete dislocation, replantation can be performed within the first 30-40 minutes, preserving the tooth unit. During the procedure, the doctor implants the dislocated tooth into its own alveolar bed and fixes it with a splinting device. The time of wearing the splint is 4-6 weeks. If the pulp is damaged, first it is removed with further filling of the canals, then under anesthesia insert the incisor into place and fix it with a splint.
Treatment of complete dislocation of teeth by replantation is applicable only to permanent units without cracks, chips on the enamel, damage to the root. Replantation with preparation takes about 40-60 minutes, the period of grafting – 2-3 weeks, sometimes more.
What to do if the tooth cannot be saved
If the peri-dental tissues and the incisor itself are so damaged that it is impossible to save it, the doctor will remove the tooth, clean the wound, if necessary, sutures will be applied. Once the jawbone has been rebuilt, options will be offered to restore the tooth through dentures or implants.