What are Zygoma zygomatic implants and why are they needed? Let’s take a look at both the pros of the system and the possible risks that patients should be charmingly aware of before deciding to have surgery.
The advent of implants has improved the quality of life for many people. Previously, patients had to make do with removable dentures that chafed, tended to fall out, and caused allergies.
Missing teeth lead to many problems:
- Chewing function is impaired;
- gastrointestinal problems;
- jaw drooping, aging of the smile;
- changes in posture due to a shift in the center of gravity;
- decreased self-esteem.
Thanks to implants, hundreds of thousands of people have not only gained a beautiful smile, but have improved their overall quality of life.
However, there has always been a large group of patients for whom conventional implants are not suitable.
An implant is a titanium post that is screwed into the bone of the jaw, in the place where the root was. As soon as we lose a tooth, that spot on the gum stops getting full nutrition. The bone begins to thin. The more time passes, the thinner the bone gets. Quite often it happens that there is nowhere to insert the post – the bone has thinned considerably. This is especially important for the upper jaw, where there is less bone tissue, because the maxillary sinuses occupy a large place there.
Implantologists offered different ways of solving this problem: transplantation or tissue augmentation, splitting of the alveolar process. But if the tissue did not take root or the surgical methods were contraindicated, patients were left with one alternative – removable prostheses.
Zygoma instead of bone grafting
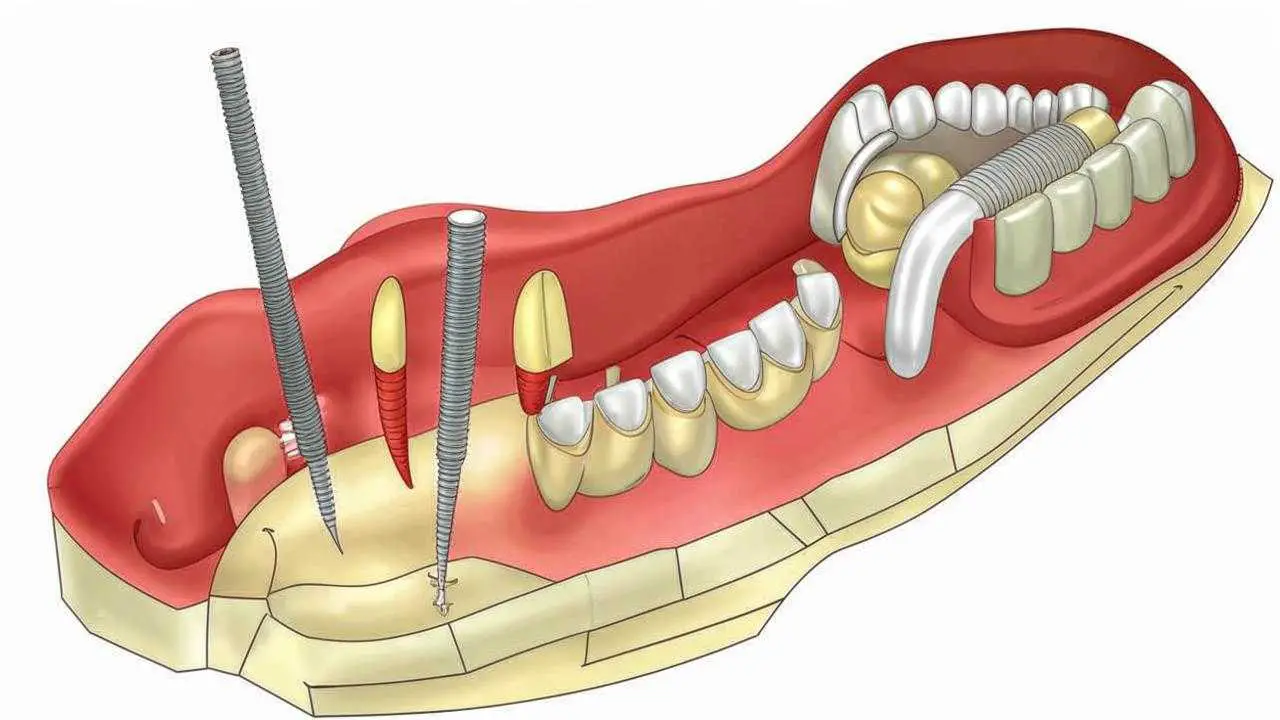
Nobel Biocare specialists have found a way out. They developed a completely new type of implants – zygoma implants. The fact is that deep bone layers are not subject to atrophy. There is enough bone tissue in them to install an implant even many years after the loss of a tooth. Implantologists and engineers have come up with super long implants that can be placed in the dense zygomatic bone. They named these implants Nobel Zygoma, from the Latin word for cheekbone.
What it does:
- implants can be placed without bone grafting;
- the list of contraindications for placement is much smaller than for conventional implants;
- more possibilities for orthopedic solutions.
Nobel Biocare has been manufacturing and installing zygomatic posts for 25 years. During this time, scientific facts have accumulated, which prove that the engraftment rate of zygomatic implants is higher [2]than conventional implants. The cortical layers are dense and provide a high level of primary stability. Zygoma zygomatic implants are not only easy to graft, but also fast – the time frame is reduced to 3 months.
Key features
- The length reaches 52.5 mm, while conventional implants are no longer than 25 mm;
- The design of the post consists of a smooth part and a screw at the end. The thread is needed to stabilize the implant in the bone, while the smooth part reduces the risk of bacterial complications;
- The special surface treatment of TiUnit accelerates osseointegration and ensures the inflow of platelets – the bone is immediately nourished and tissue metabolism begins.
Who Zygoma implants are suitable for
The main indication for the installation of zygomatic implants is bone atrophy. Therefore, such implantation is recommended:
- Cancer patients. Zygomatic pins have been developed also for cancer patients with bone loss caused by chemotherapy and radiation therapy.
- When bone atrophy occurs as a result of medical manipulation or as a consequence of trauma
- After unsuccessful bone grafting or impossibility to perform it
- In the case of severe bone resorption and complete adentia
- In osteoporosis
- Periodontitis stage 3-4
- If there are contraindications to implantation with conventional posts.
How Zygoma zygomatic implantation works
Zygomatic implants are used only in full jaw prosthetics. This is, for example, the usual All-on-4 system from Nobel, but only instead of classic implants, zygomatic implants are used.
- Diagnosis. Do not think that zygomatic implantation is suitable for everyone. Whether it is worth putting Zygoma is decided by the implantologist based on CT data, tests and anamnesis. Only after analyzing all the information is the decision to place implants made.
- Modeling using a special program. The software for implant placement allows to create an accurate 3D model of the jaw, on which the places for insertion of pins are already marked.
- Implantation itself. During the operation modern anesthetics are used, which completely exclude painful sensations. The implantologist makes incisions in the gum and screws in the implants.
- Prostetik. Zygoma – implants with immediate loading. A temporary jaw is placed immediately. Loading it stimulates blood circulation and metabolic processes, accelerating osseointegration.
- Final stage. Once the osseointegration process is complete, the permanent denture is fitted.
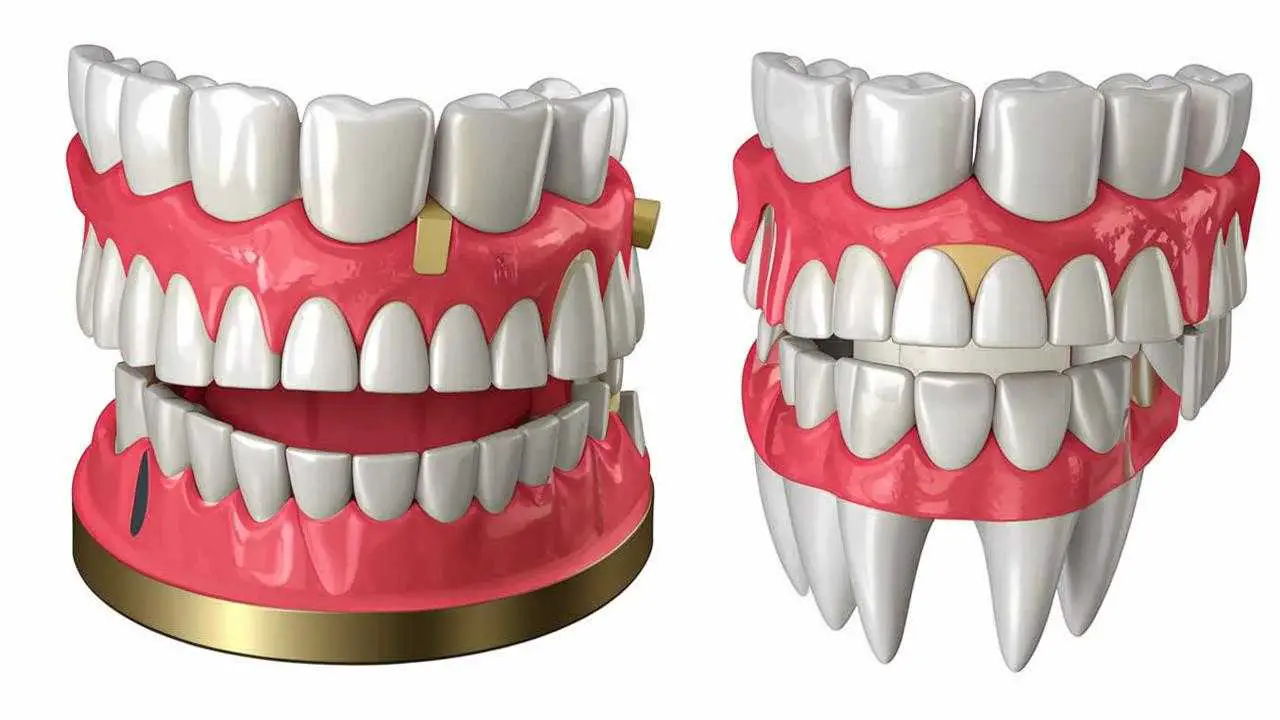
Two options for prosthetics with Zygoma implants
Risks
Zygoma implants are long, they run along the edge of the maxillary sinus and come close to the nerve endings and eyes. Placement of these implants requires jewel-like precision from the oral surgeon.
Common complications:
- Sinusitis. A titanium post can provoke inflammation of the maxillary sinus.
- Rejection. The rate of engraftment of zygomatic implants is high [2]However, some of them do not take root and complex surgery is wasted.
- Fistula formation. A fistula is a “passage” between the oral cavity and the sinus. Through it, microbes penetrate into the sinus and cause inflammation.
- Paresthesia (feeling of goosebumps on the skin). If the doctor touches the suborbital or zygomatic-facial nerve during implantation, paresthesias of a long-term nature may result.
- Trauma to the eye socket. A rare complication caused by surgeon’s error.
- Complications of TMJ (temporomandibular joint).
Undoubtedly, zygomatic implants are a breakthrough in dentistry, but their installation requires vast experience, special training, and modern equipment. Complications after surgery can develop into a serious problem. The psychological factor cannot be excluded. Many patients, having seen a photo of the jaw with such pins, literally panic. Therefore, implantologists offer alternatives:
- removable prosthetics;
- bone grafting;
- pterygoid implants.
What are pterygoid implants?
In the course of scientific research, it became clear that bone density is maintained at a high level not only in the cheekbones, but also in the wing ridges. Then they developed implants that are shorter than zygomatic implants, but long enough to be placed in the wing process. These pins were called pterygoid (wing pins).
Due to their short (compared to zygomatic) length, pterygoid placement is less traumatic and the risk of complications is much lower.
Tanda-tanda
| Pterygoids
| Zygoma |
Material | Medical titanium | Medical titanium |
Length | 16-24 mm | 30-55 mm |
Place of insertion | Prygus of cuneiform bone | Malar bone |
Safety level of the procedure | High | Medium |
Pin design | Threading on all surfaces for better contact | Thread at the very end of the pin |
Risk of complications | Minimal | High |
The special threading on pterygoid implants promotes bone compaction along the course of the screw. The advantage of this screw is its high primary stability and rapid osseointegration.
The implant engraftment rate of pterygoid implants is 99% [1]
In other respects, pterygoid and Zygoma are similar: they are placed in cases of significant bone loss, used as an alternative to bone grafting, have a short engraftment period, and are suitable for immediate loading. Except that the price of Zygoma implants is much higher.
The cost of pterygoid and its safety makes it an attractive alternative to zygomatic implants.
To find out what type of implantation will suit you exactly, you can consult with a specialist. They are performed free of charge in most dental centers in Moscow.
Sources:
[1]https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25830398/
[2]https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23078128/