Reading time ~ 5 min Number of readings: 17193
Gingival recession is a process of gum tissue loss in which the root neck of the tooth is exposed. Visually it looks like this: due to the exposure of the root part, the teeth seem longer, and a small groove is formed on the edge of the gum. The sensitivity of teeth to acid, sweet, salty and temperature changes increases. Gingival recession can be observed in the area of one tooth or several. However, to establish an accurate diagnosis, it is necessary to consult a dentist.
Classification
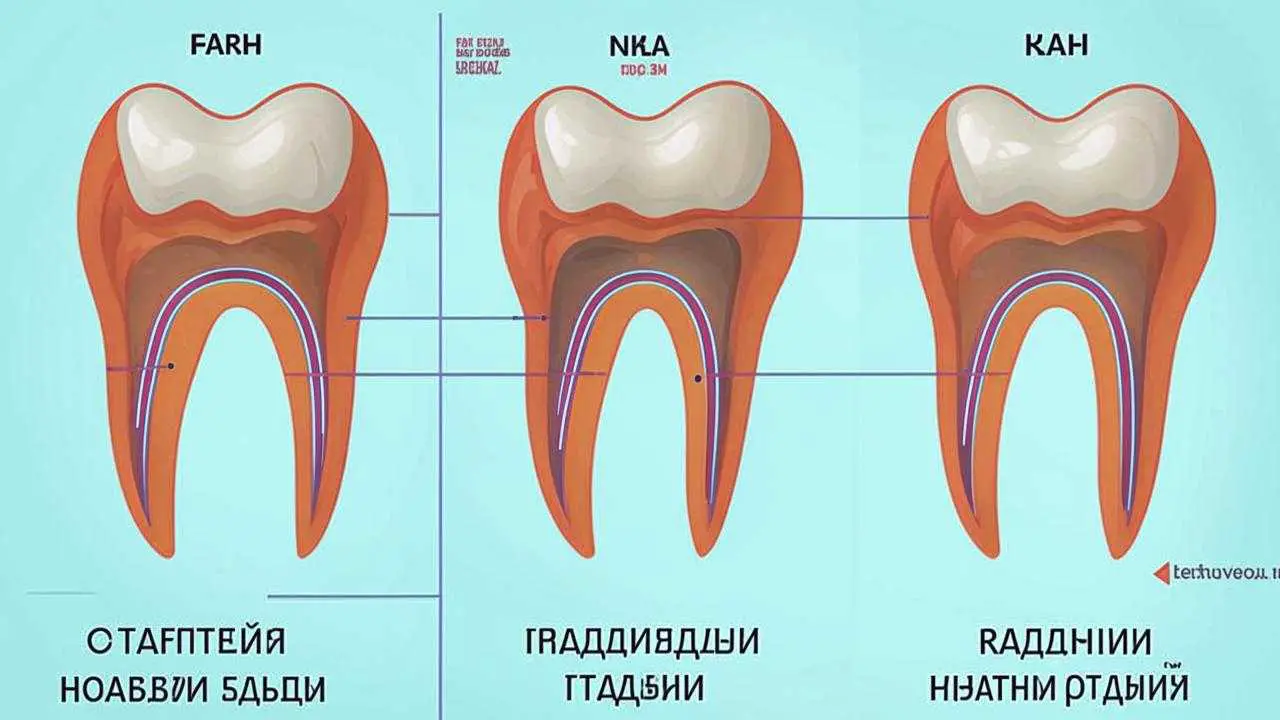
Depending on the preservation of gum tissue, there are 4 stages of gum recession:
- In the first stage, only the attached part of the gum tissue is reduced. The reduction in tissue volume is insignificant.
- The area of attached gingiva is destroyed, but bone and gingival tissue are preserved, and tooth sensitivity increases.
- At the third stage, the outer surface of the tooth is exposed, tooth sensitivity becomes painful.
- The tooth is exposed around the perimeter, including in the place of interdental spaces.
Gum recession is a gradual process. In most cases, it is caused by a specific dental disease. The gum thins and shrinks, resulting in tooth mobility, loosening, which can lead to tooth loss.
Causes of gum recession
A variety of factors can cause gum recession. Self-diagnosis is the first step to identifying the problem so that you don’t pay too high a price for inattention. Below are the most common causes of recession:
- Improper oralhygiene. For example, too aggressive brushing: using a hard toothbrush, mechanical damage during dental care;
- Lack of oral care. If plaque is not brushed off, it will lead to the formation of tartar, which in turn causes gum disease and recession;
- periodontal disease. This gum disease is often accompanied by recession. If not treated in time, it will lead to tooth loss;
- natural aging of the body;
- bad habits: biting lips and nails, biting pens, pencils, smoking;
- traumatic, sloppy dental treatment, including whitening procedures.
In addition, predisposing factors can be peculiarities of the structure of the oral cavity, jaw (pathology of the bite, location of individual teeth, shortened frenulum of the lips and so on) and somatic diseases (metabolic syndrome, diabetes mellitus, etc.).
Diagnosis and consequences of gum recession
Timely diagnosis of gum recession contributes to the early elimination of the problem and prevention of the development of unpleasant consequences. To perform an independent diagnosis, it is necessary to know the following symptoms:
- the gum is red and inflamed;
- some teeth look longer than others;
- there are gaps between the roots of the teeth, which continue to increase;
- there is high tooth sensitivity;
- bad breath is present.
If one or more signs are detected, it is necessary to urgently contact a dentist to immediately begin treatment of gum recession. Otherwise, in addition to physical discomfort, the risk of tooth decay and pulpitis increases. This is due to active bacterial growth in the root part of the tooth, where the enamel is the least thick. Eventually, if the process is allowed to go unchecked, it will lead to loose teeth and even tooth loss.
The more neglected the disease, the more complicated the treatment and the more the cost of such surgery increases. Therefore, it is not worth delaying a visit to the clinic.
Treatment of gingival recession
Depending on the degree of gum recession, there are several ways of treatment:
- Medication. This method of treatment is applicable in the first and second stages. The attending physician prescribes a course of antibiotics or drugs to strengthen immunity, relieve inflammation, improve blood circulation. This can also include rinsing the mouth with various medicinal tinctures, rubbing medications (gels, ointments) into the gums.
- Physiotherapy. Basically, these are procedures aimed at improving the blood circulation of the gums and their nutrition. Namely: gum massage, tocotherapy, laser therapy, ultraviolet radiation.
- Plasmolifting. In this case, a composition derived from the patient’s blood is injected into the gum. Plasma contains unique components that help to restore tissues as soon as possible.
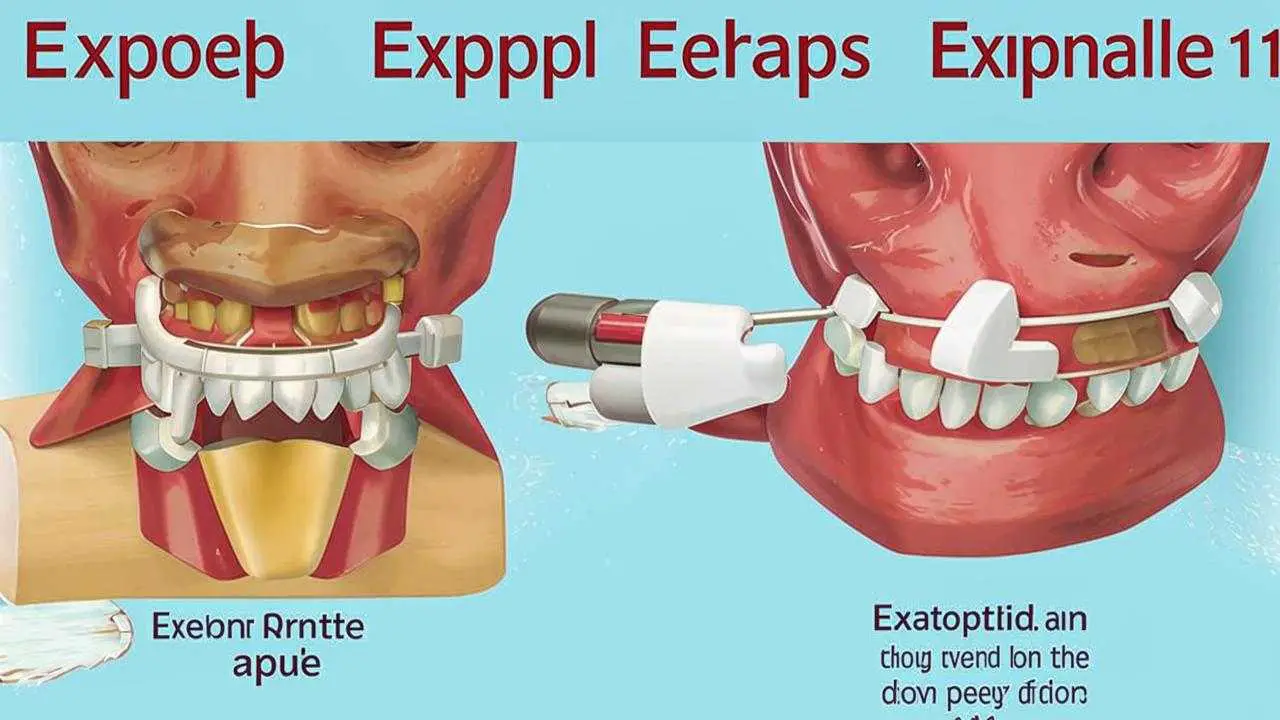
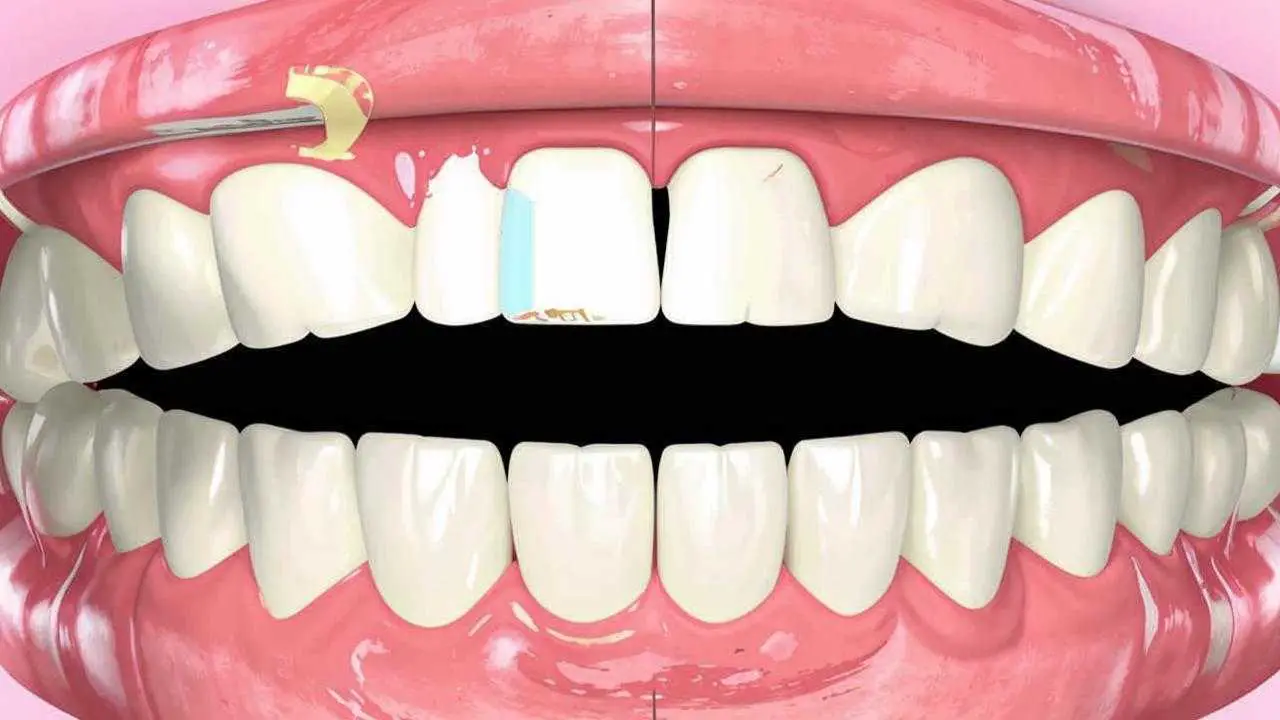
- Surgical intervention. This method includes flap surgery, in which the gum recession is closed by cutting the gum tissue and cleaning the root canals. In some cases, a layer of healthy palate is removed to restore the missing biomaterial. Once the flap surgery is complete, it is often necessary to perform an additional procedure called – gum recession plasty. It is needed in order to restore the natural appearance of the gum. This is a fairly simple and quick manipulation, which completely restores the aesthetics of the smile.
- Regeneration. A surgical procedure to build up damaged soft tissue. First, the bare area above the gum line is cleaned, then a material that stimulates tissue regeneration is applied. For example, a membrane or graft. This promotes the growth of gum bone and tissue in the damaged area. Next, the gum is fixed to the root of the tooth.
A combination of the above methods will ensure that gum tissue recession is quickly restored and prevent recurrence.
Preventing the development of gum recession
Like any disease, gum recession is easier and cheaper to prevent than to think about how to stop the process that has already begun. All of the above methods of eliminating gum recession will not be needed if you carry out timely prevention of this disease. Namely:
It is very important not to allow the development of inflammation and the attachment of infection in the oral cavity. To do this, it is necessary to use drugs with anti-inflammatory action as a means of rinsing or brushing teeth.
With proper care, your teeth and gums will last you for many decades and will not cause you any trouble. And going to the dentist will only be a routine visit.