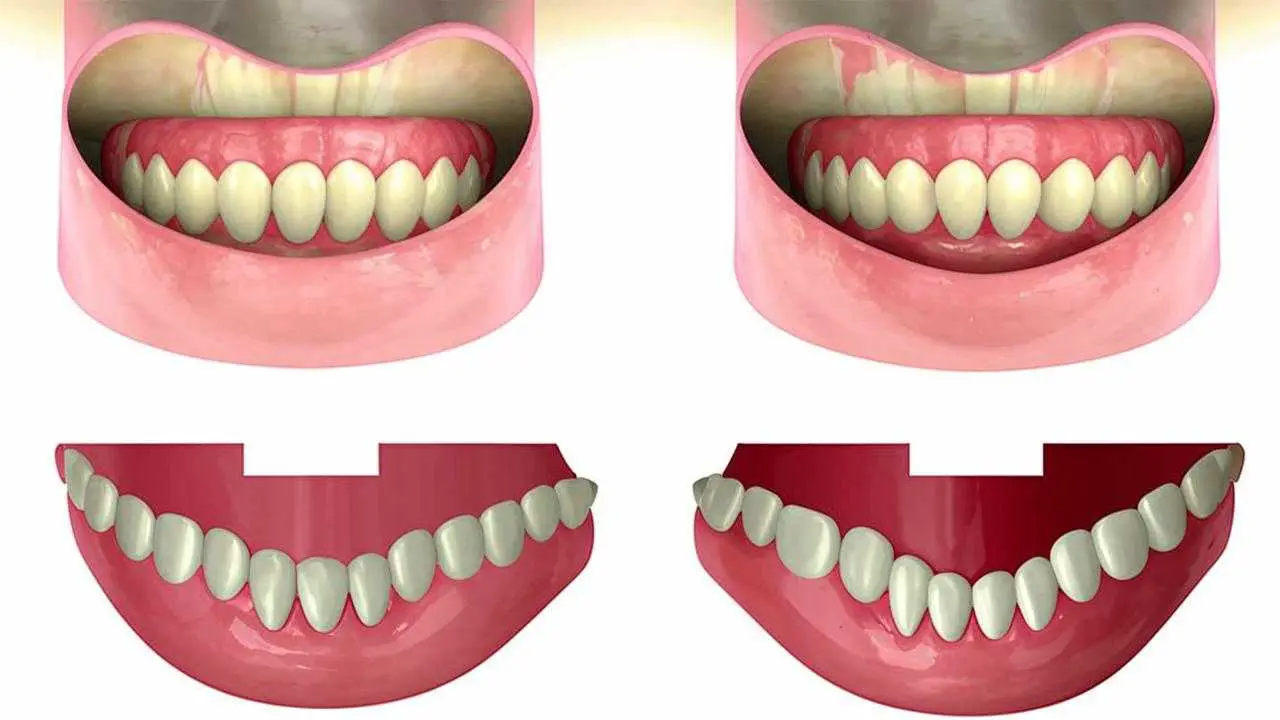
Gum hyperplasia is a condition in which tissues begin to overgrow. They overhang over the teeth, forming false pockets, cover most of them, preventing hygiene procedures. In the literature there are several terms describing this condition: gingival overgrowth, hypertrophy or hypertrophic gingivitis.
The main danger of tissue overgrowth is that it promotes the multiplication of bacteria, provoking serious diseases such as periodontitis.
Causes of gingival hypertrophy
The main cause of tissue hypertrophy in the mouth is poor hygiene. Food residues, decay products settle on the enamel of the teeth. They accumulate, causing inflammation of the mucosa, one of the manifestations of which is hyperplasia.
Other causes include:
- Taking certain medications
A side effect of some anticonvulsant drugs and immunosuppressants, certain cardiac drugs is gingival overgrowth. However, you should not interrupt their intake or reduce the dosage, if the gum has increased in size and began to bleed, without consulting a doctor.
- Genetic predisposition
Most people experience tissue overgrowth during puberty. In most cases, after the end of hormonal restructuring, there is a spontaneous reduction. But in some patients, the gingiva does not decrease, and may even increase in size. Such a phenomenon is characteristic of hereditary fibromatosis.
- Common diseases
Leukemia almost always provokes hypertrophy of tissues, because they are impregnated with dense masses of immature leukocytes. The gingiva turns into a hard, surface on which wounds occur at the slightest pressure. This problem is also characteristic of sarcoidosis.
- Hormonal instability
Pregnancy, diseases of the endocrine system, such as diabetes or hypothyroidism, disrupt metabolic processes in tissues, lead to inadequate growth.
- Teeth crowding
If the teeth overlap each other, overlapping surfaces, this prevents the proper cleaning of surfaces, contributes to the formation of microbial plaques. These, in turn, provoke inflammation.
Symptoms
Overgrowth of the mucous membrane is a gradual process. 3 degrees are distinguished:
- Gingival papillae increase in volume. The gingival contour is broken, overhanging the tooth.
- Overgrowth progresses, the tissue covers up to half of the crown part. There is bleeding, unpleasant sensations when brushing and eating.
- The gingiva covers the tooth by two-thirds, sometimes completely. Folds are formed, in which microflora accumulates, provoking inflammation.
The process can be generalized, when the entire gum on the jaw suffers. Focal hyperplasia is located around one or more teeth.
The edematous form is characterized by the presence of plaque, there is a lot of it, it is quite soft, but covers the enamel with a thick layer. Gingival pockets are formed. The papillae turn red, bleed when pressed.
Patients complain of itching, unpleasant sensations in the mouth while eating, unpleasant odor.
With fibrous hyperplasia of the gingiva, patients are bothered only by the unusual appearance of the mucosa. Pain and bleeding are usually absent, but there are complaints of unpleasant odor.
Treatment of gingival hyperplasia
Any medical intervention is preceded by diagnosis. In the clinic, a visual inspection is carried out, using dental instruments. Do x-rays, in some cases, tissue biopsy. Collect information about current diseases, what medications the patient is taking.
Gingival hypertrophy is differentiated from papillomas, granulomas, epulis (neoplasm) or gingival edema due to periodontitis.
The treatment plan is based on the extent, course and cause of the gingival overgrowth.
In case of concomitant diseases, the procedures should be coordinated with the attending physician. Sometimes, a simple change of medication can reduce the overgrowth.
Therapeutic methods
Are used mainly after changing the medication that caused the hyperplasia.
- Decoctions and applications of oak bark, chamomile, St. John’s wort, calendula. Tannins in these plants narrow and strengthen the walls of blood vessels, reducing their permeability. As a result of combining with proteins, tannins form an insoluble film on the mucosa. This protects nerve endings from decay products and reduces pain.
- Installations into gingival pockets. Plant-based preparations are placed in the pockets for 15-20 minutes, for up to 3 weeks.
- Dorsenval therapy. After the elimination of the inflammatory process, physical procedures are carried out to strengthen the blood vessels.
The main therapeutic measure is professional cleaning of the teeth.
If the effect of the procedures is insignificant, as well as with fibrous hyperplasia, gingivectomy is performed.
Surgical treatment
In cases where the gum has grown on the tooth so that it covers half of the surface or more, the excess tissue is removed. In fibrosis therapeutic treatment is not used at all, in other cases the decision depends on the clinical picture.
The operation is performed under local anesthesia. Apply:
- Classical method. Tissue is dissected with a scalpel. The surface of the roots is polished with instruments, the wound is treated with antiseptic. Finally, a special dressing (septopak, vokopak) is applied.
- Removal of overgrown gum with a laser. This is a minimally invasive operation, after which healing is much faster. Vessels during the operation are sealed with a laser beam, which eliminates bleeding. At the same time destroyed pathogenic flora. After such operations, complications are extremely rare.
Complications
Hyperplasia is dangerous because without treatment it provokes inflammatory processes in the periodontium: gingivitis and periodontitis. This leads to loosening of teeth and their loss.
Due to the fact that it is impossible to clean the teeth well, caries often develops. There is demineralization of enamel. Metabolic processes are disturbed.
Due to increased sensitivity, patients try not to chew on the side where the gum has grown. Chewing load is distributed unevenly, the risk of tooth loss increases.
Prevention
Simple measures can help prevent gum overgrowth. Dentists recommend brushing with a soft toothbrush, flossing, or using interdental brushes. Using a mouthwash reduces the amount of bacteria deposited on the enamel. But all these measures won’t help if there is plaque on your teeth. So a professional dental cleaning at the dentist, that’s where hyperplasia prevention begins.