Χρόνος ανάγνωσης ~ 6 min. Αριθμός αναγνώσεων: 82533
The viability of the tooth, in particular its sensitivity, provides the neurovascular bundle (pulp). Removal of the pulp (depulpation) is a forced measure, which is resorted to for serious indications (pulpitis, root cysts, damage to the pulp chamber due to trauma, etc.). Painful discomfort for several days after depulping is a normal reaction of tissues to the intervention. But if the tooth hurts after nerve removal and canal filling 2-3 weeks later, or if the pain occurs sharply long after endodontic treatment – this is a serious reason to consult a dentist.
Even treated teeth should be examined every year to diagnose or rule out complications at an early stage. A depulped tooth doesn’t hurt, but it’s like a ticking time bomb. Poor treatment of canals can provoke complications that destroy the jawbone, cause purulent processes (cysts, abscesses), life-threatening. Properly treated canals are the foundation of any restoration. The more modern and high-quality materials for their treatment – the less likely complications.
Can a tooth hurt after a nerve extraction
A tooth from which the nerve has been removed is called a “dead” tooth. Logically, a tooth without a nerve cannot hurt. But the tissues after endodontic treatment need time to recover. Therefore, reactive pain after treatment of a tooth can normally persist for several days. Over time, it weakens and passes on its own. Usually, painful sensations occur when pressing or eating – they can persist for 1-3 days, maximum a week.
A completely different picture, when the pain increases, becomes throbbing, the gum is swollen, red, swollen, there are symptoms of intoxication – headache, fever, weakness. Such symptoms indicate the development of complications, require immediate contact with a dentist. The doctor will establish why the dead tooth hurts, will carry out effective treatment.
Reasons why a tooth hurts without a nerve
- Re-infection – not all the affected tissues were removed, the source of infection remained, and the inflammation began to spread again. This can happen if endodontic treatment is performed without a dental microscope or the tooth canals have a very complex structure, which did not allow their qualitative cleaning, disinfection.
- Poor-quality filling – when filling in the canal left voids in the canal, not filled with material areas in which pathogenic microorganisms begin to multiply, which leads to inflammation, periodontitis, cyst formation, granuloma.
- Exit of filling masses beyond the root apex – filling material coming out through the apical hole, hardens in the periodontal tissues, compresses nerve endings, disrupts blood circulation. Inflammation develops in the periodontium, accompanied by severe pain.
- Perforation of the canal walls – in the area of perforation the dental tissue becomes infected, inflamed, when filling, the composite may leave the canal boundaries.
- Incomplete depulping – due to the complex structure of the canals one of the nerve endings could not be removed by the doctor. The use of a dental microscope with good optics significantly improves access to the prepared cavity and facilitates the detection of the mouth of the canal, all nerve branches.
- Instrument breakage in the canal – during reaming, cleaning, filling a piece of instrument could break off and remain in the dental canal. The presence of a foreign object contributes to the formation of voids, where conditions are created for the multiplication of bacteria and the development of inflammation.
- Allergy to filling materials or medication, accompanied by pain, swelling, discomfort in the area of the dental unit.
- Over-height filling – the opposite tooth (antagonist) exerts excessive pressure on the filling, which leads to the appearance of painful symptoms.
- Affection of the neighboring unit – the soreness spreads (irradiates) along the gum from the neighboring tooth.
Possible complications
- Periodontitis;
- formation of granuloma, root cyst;
- periostitis (flux);
- Complete destruction and/or loss of the tooth;
- osteomyelitis.
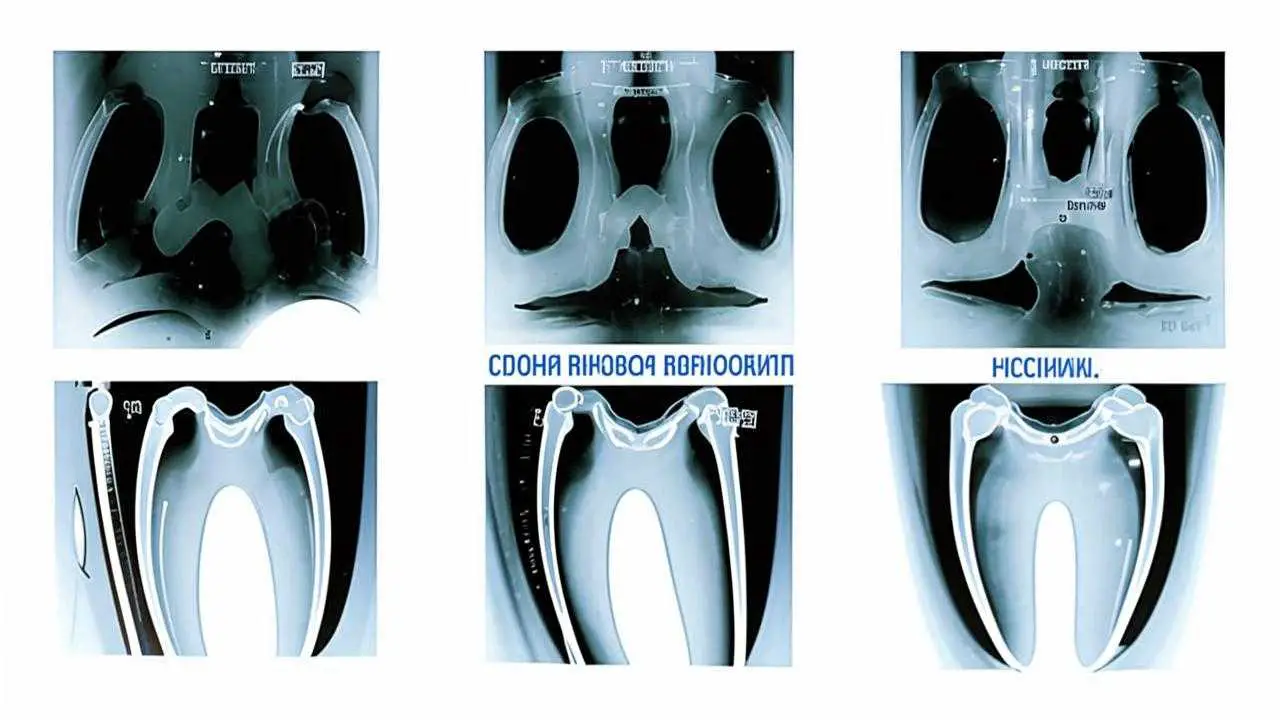
To exclude complications associated with poor-quality endodontic treatment, the RUTT Clinic in Moscow conducts control radiography, uses an apex-locator to assess the depth of the canals. The use of computer tomography, operating microscope provide more opportunities for accurate diagnosis and quality treatment.
What to do if a depulped tooth hurts?
Soreness after depulping is a normal tissue response to the intervention. But such symptoms should go away in a couple of days after endodontic treatment. If the tooth canal without nerve hurts and the pain does not subside, but on the contrary increases, it is necessary to consult a dentist. The pain can be different – pressing, aching, pulsating, radiating to the eye socket, temple, cheek. In addition to pain, there may be redness, swelling. Allergy to the material or antiseptic preparation is usually accompanied by burning, fever, general weakness, a feeling that the tooth “rises” above the neighboring units.
The deeper the pathological process has gone, the more pronounced the symptomatology. Once the inflammation has moved to the periodontium, a person begins to feel pain when biting, pressing on the tooth. When pus accumulates on the gum, a fistula is formed, through which the outflow of purulent contents is provided, temporarily alleviating the condition. The presence of a fistula is a direct indicator that there is a problem with the roots of the tooth.
The doctor will conduct a diagnosis, will establish the exact cause of pain. To do this, an examination is carried out, a number of X-ray examinations are performed:
- targeted images of the affected tooth in different projections;
- orthopantomogram;
- 3d-tomography.
The therapeutic tactics doctor selects according to the clinical picture. If the pain occurred against the background of repeated infection, allergy to the material, errors in the primary treatment, carry out repeated treatment – open the root canals, processed and filled. If painful sensations are caused by pulpitis or deep caries of the neighboring dental unit, it is treated. Cysts, flux, osteomyelitis are treated surgically – the gum is cut, cleaned, the affected areas are removed along with part of the tooth root (if indicated). If the dental unit is inexpedient to save, it is carried out its removal with subsequent prosthetics.
How to relieve pain
If the tooth hurts badly after pulpitis treatment, temporarily relieve the pain symptom and relieve the condition will help to take an anesthetic (Analgin, Ibuprofen, Ketolak, etc.), mouthwash with antiseptic solution or warm herbal decoction of melissa, sage, oak bark, chamomile, calendula.
It is strictly forbidden to warm the sick tooth, apply alcohol, garlic compresses to the gum, take antibiotics and aspirin preparations.
Prevention of complications
- Regularly come to see the dentist, immediately contact if the tooth hurts after cleaning the canals;
- immediately consult a doctor if there are signs of allergy to the filling material, increasing pain, fever, swelling of the gum or face;
- follow the doctor’s recommendations after endodontic treatment regarding oral care, taking medications;
- do not self-medicate.