Reading time ~ 6 min Number of readings: 40034
Tooth restoration is a multi-step process. First, a diagnosis is made. Then carry out a system of preparatory measures: treat tooth decay, remove plaque. Part of this process is depulping the tooth before prosthetics.
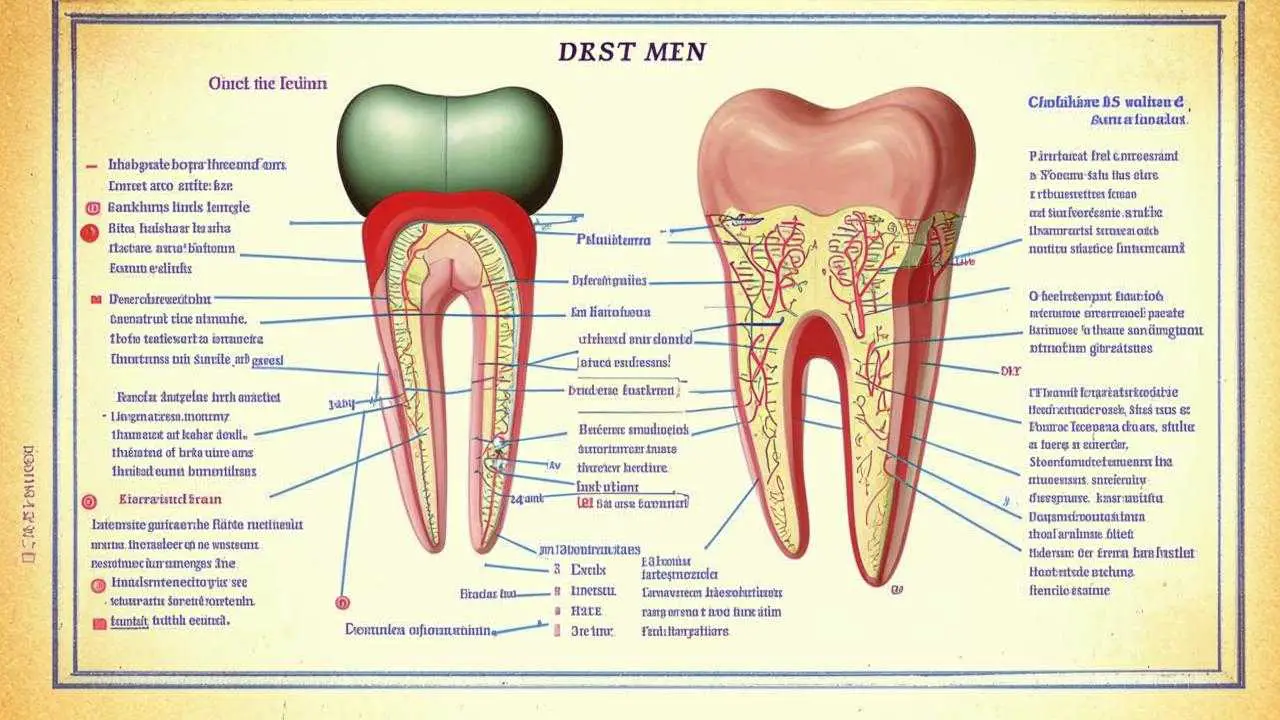
Depulping is the removal of the pulp, the tooth tissue that is permeated with nerve endings and blood vessels. The blood vessels supply blood, nutrients, and nutrients to the tooth. Nerve endings signal pathological processes, helping to save the tooth by treating it in time. In addition, the pulp is involved in the formation of dentin, the supporting tissue of the tooth.
When depulpation is performed before prosthetics
Not so long ago, nerve removal was a routine process prior to the placement of fixed structures. Recently, the views of dentists have changed. The fact is that a tooth without a pulp is considered “dead”. There is no tissue exchange there, secondary dentin is not produced. It becomes brittle. In addition, when there is no pulp, the inflammatory process can completely destroy the tooth, because there will be no pain for a long time.
On the other hand, if the pulp becomes inflamed under the crown, the expensive and complex restoration will have to be removed for treatment.
There is no unanimous opinion whether it is necessary to remove the nerve during prosthetics among dentists. Each point of view has its defenders and opponents. The golden rule of dentistry is to carry out the manipulation strictly according to indications.
Indications for removal
The more tissue is removed in the preparation of the tooth, the higher the risk of opening the pulp chamber. To avoid this, the nerve is removed before prosthetics. This is also done if:
- in the presence of a large cavity that would make the dentin layer too thin to perform its protective function after preparation;
- if the teeth are extended or lengthened;
- tilted, rotated or abnormally positioned teeth;
- in individual cases in patients with periodontitis;
- in case of increased erosion of teeth of the 2nd to 3rd degree;
- when using large-volume inlays;
- in case of increased tooth sensitivity that persists after treatment;
- when the neck of the tooth is exposed as a result of gingival recession (loss).
In these cases, the pulp is removed even with healthy teeth. Also, the manipulation is carried out in case of root fracture, multiple caries and pulpitis (inflammation of the pulp).
In what cases it is not worth removing the nerve
Depulpation before dentures is contraindicated in the following conditions:
- hypertensive crisis;
- myocardial infarction;
- jaw misalignment due to various causes;
- epilepsy;
- mental disorders that make contact difficult.
How a tooth is depulped prior to dentures
It is up to the doctor to decide whether or not to depulpate a tooth. The main method of diagnosis is an X-ray. It shows the presence of inflammation, the condition of the roots, the thickness of dentin. Another method is visual inspection, where the condition of the oral cavity is assessed, the physical location of the teeth. Based on clinical data, a treatment plan is drawn up. If it is decided to remove the nerve before prosthetics, the procedure follows the following algorithm:
- Anesthesia. Most often it is an injection into the gum. In individual cases, sedation can be carried out.
- Removal of the affected tissues. If there is no caries, this stage is skipped.
- Opening access to the pulp and canals. To do this, the dentist has to remove part of the hard tissues – enamel and dentin.
- Removing the pulp from the pulp chamber. This is a simpler stage.
- Extracting loose pulp from the canals. This is a complex stage. Manipulation is carried out blindly, the skill of the doctor depends on how thoroughly he cleans the canals.
- Treatment of the canals with antiseptic solution
- Drying the surface
- Filling the canals. This is done to prevent the penetration of pathogens into the canal.
- Applying a gasket to isolate the canals. For this purpose, dental cements of different types are used.
- Temporary filling. It is necessary only in the case of the application of medication. A temporary filling is placed for a period of up to 14 days. It can be easily removed if complications arise and additional treatment is needed. If there are no problems, proceed to the next stage.
- Replacing the temporary filling with a permanent one. Filling is carried out with durable composite materials.
- Grinding off the excess filling.
- The finishing touch is the polishing of the filling.
This is a vital removal. No preliminary manipulations with the neurovascular bundle are not carried out, amputated on the living.
The devital method involves mummification of the pulp with its subsequent removal. After access to the pulp is opened, a paste containing paraformaldehyde is put in the hole. Or, as they say, arsenic. Then the paste is carefully isolated, closed with a temporary filling and wait for the nerve-vascular bundle to mummify. After 3-7 days, again open the cavity and remove the pulp. The canals are treated and filled. This method is rarely used because of the risk of toxins getting into other tissues.
In the process of work, control pictures are taken to monitor the quality of canal occlusion.
Complications
The most common complications after nerve removal before dentures are pain and swelling. Normally, these symptoms go away after a day at most. If the pain does not let go, increases, swelling does not go down, you need to see a doctor. He will conduct diagnostics to identify the causes. It can be:
- Poor quality cleaning of the canals. Improperly selected length of the instrument does not allow you to pass the canal to the end. Remains of pulp cause inflammation – residual pulpitis.
- Perforation of the root canal. Through the destroyed apex, the infection penetrates into the periodontium (the tissue around the tooth), causing pain.
- Missing tooth canals. X-rays don’t always show all the canals, and this is the only source of information for the dentist. Remnants of the pulp become inflamed, being a source of discomfort.
- Tooth fracture. If the anatomical shape of the tooth is not restored immediately, it can break.
- Violation of filling technology. This may be incorrect proportions for mixing the composition or getting the filling material on soft tissues.
Sometimes, after endodontic treatment, the tooth darkens. Without the pulp, nutrition is not supplied to the tooth, cells are not renewed. The dentin dries out, and its color darkens. Another reason is that enamel becomes porous and pigments can penetrate through it more easily. Sometimes, the tooth darkens due to hemorrhage when the nerve is removed before prosthetics.
Do not be alarmed, it is not dangerous. The denture will provide a protective barrier and hide the discoloration.
The nerve has been removed, what happens next
Recommendations after depulping include the following advice:
- reduce physical activity for the first 2 hours after nerve removal;
- refrain from eating for 2-3 hours;
- make soothing, herbal and salt baths;
- apply ice.
Do not refuse to depulp the tooth before prosthetics, if there are problems, the price and complexity of treatment of the tooth with removal of the prosthesis will be much higher. Observance of general hygiene rules and regular visits to the dentist will help to prevent infections and inflammations and save your teeth for a long time.