How to choose? Acryl AcryFree Nylon AcryFree Nylon Polymer Comparison Metal Ceramics Metal Plastics Ceramics Zirconia Zirconia Fixed Denture Comparison Composite Doctors Jobs
Although prosthodontics as a science was formed not so long ago, people have been practicing dentures since antiquity. Animal bones, semi-precious stones, hard wood – what only ancient physicians did not use as a material of prostheses. But the methods of fastening were rather monotonous – with the help of gold, rarely silver, wire.
What are dentures made of now? The composition for prosthetics is selected for a specific clinical case, taking into account the patient’s wishes, indications and contraindications.
Basic requirements to the material for dentures
Although a wide variety of materials are used in prosthetics, all of them must meet certain requirements: to be durable, functional and attractive in appearance. This is why gold crowns and iron teeth are a thing of the past. Alas, there is no such thing as an ideal alloy. Usually, the more brittle ones mimic natural enamel better than the harder ones. But orthopedists strive to strike a balance in everything. Regardless of what materials dentures are made of, they should:
- Withstand exposure to harsh environments. Sour, sweet, salty – these are all chemical irritants that negatively affect the denture. Retain their function despite unfavorable environments – one of the important requirements for the composition.
- Do not interact with food and change its flavor
- Be comfortable to wear
- Look natural
- Have no odor or taste
Polymers (plastics)
The use of polymers in orthopedics has been a revolution. Plastics are still one of the most sought-after prosthetics. Polymers are most often used for the fabrication of full or partial removable prostheses and as temporary structures.
Acrylic
This is an inexpensive, lightweight plastic. It is resistant to chemical influences and holds its shape well. Acrylic dentures are easy to make, they can be repaired. Unfortunately, it is hygroscopic, easily covered with microcracks, in which bacteria accumulate. It takes a long time to get used to acrylic systems, and they often cause discomfort. These disadvantages are easy to accept, but acrylic plastics contain monomers, substances that cause allergic reactions. This is the main disadvantage of acrylic. An allergy test is mandatory before prosthetics.
Nylon
The problem of allergies is solved by thermoplastics – plastics that have no monomers. The most common of these is nylon. It is very strong, but at the same time elastic. It does not lose its color even after several years of use. Systems made of nylon do not rub the mucosa, take up little space in the mouth. You get used to them faster than to acrylic ones.
But nylon as a removable denture material also has disadvantages. Because of its flexibility, nylon can easily detach from the palate. The chewing load is not evenly distributed. Nylon is more difficult to work with and is not available everywhere.
AcryFree
Technologists have long tried to find the golden mean between acrylic and nylon, and they succeeded. The modern denture material AcryFree combines the advantages of both polymers. It is stiffer than nylon but softer than acrylic. The moderate stiffness provides an even load when chewing. Although AcryFree cannot stop bone loss, it significantly slows bone loss. Thermoplastic does not contain monomers, which means it does not provoke allergic reactions. The manufacturing method is injection molding, which eliminates the formation of micropores.
The disadvantages include a long period of habituation, the need for special care, the risk of breakage of clasps.
Comparison of polymers
| Properties | Acryl | AcryFree | Nylon |
| Presence of allergens | Yes | No | No |
| Price | Lav | Medium | Høj |
| Elasticity | Lav | Medium | Høj |
| Breakage probability | Høj | Medium | Lav |
| Possible repair | Yes | Yes | No |
| Risk of loosening of neighboring teeth | Høj | Lav | Lav |
It is up to the patient and the doctor to decide which one to choose after an examination.
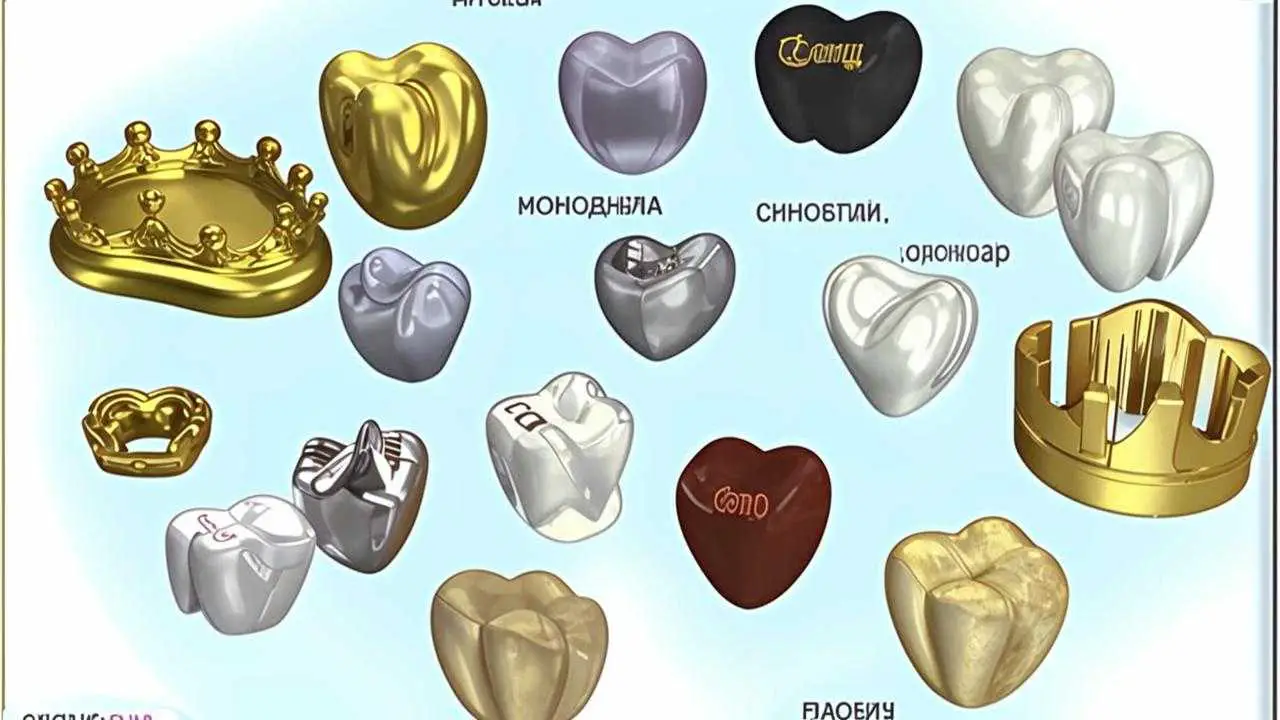
Metals
Metal alloys are used in partial removable prosthetics, such as braces. This is usually an alloy of chromium with cobalt or nickel, but sometimes titanium is used.
It is common to use metals as a material for fixed prostheses: crowns and bridges. They are made of precious metals: gold, platinum, palladium or the above mentioned alloys. Metals are also used to make inlays.
Metal-ceramics
Nowadays, metals and their alloys are mainly used as a framework for metal-ceramics.
Metal cladding with ceramics solves the main problem of metal constructions – galvanosis. Reacting with each other metals cause a chemical reaction, which is expressed in a metallic taste in the mouth, irritation of mucous membranes, burning of the tongue. Ceramics insulate the metal, preventing galvanization. Noble metal constructions are bioinert and do not cause galvanization.
The main disadvantage of metal-ceramics: the metal shines through and the tooth does not look natural. In addition, the place of connection with the gum often turns blue, which spoils the impression of the smile. Therefore, metal-ceramics is preferred for chewing teeth, where aesthetics is not as important as durability.
Metal plastics
It is used for temporary crowns. The base is made of metal and a plastic overlay is placed on top. Quality crowns can last 2-3 years, but eventually they will have to be replaced. They are fragile, easily stained and cracked.
Ceramics (dental porcelain)
To solve aesthetic problems and reduce the risk of galvanosis, ceramic products help. Conventional dental porcelain is too fragile, so technologists have developed innovative materials:
- Empress, a glass ceramic based on leucite;
- lithium disilicate-based glass-ceramic – E-max;
- microceramics based on zirconium silicate – Ceramage.
Dental prostheses made of ceramics:
- imitate tooth enamel in color and light refraction;
- do not cause allergic reactions or galvanosis;
- thinner than metal dentures, so teeth are not ground down as much;
- do not require depulping;
- fit tightly to the gums.
Zirconium dioxide
A special feature of zirconia is its hardness. It is the strongest dental compound. It can be used on chewing teeth. Zirconium is an inert material, it is hypoallergenic, does not cause irritation. Zirconium products do not conduct heat and cold well, they will help patients with hypersensitive teeth.
Zirconium dioxide does not transmit light as well as glass-ceramic, so it stands out with a special whiteness. The disadvantages include the ability to rub off the antagonist teeth.
Metal-free compositions are used for the fabrication of bridges, crowns, veneers, inlays.
Comparison of compositions for fixed dentures
| Functions | Metal-ceramic | Metal-free compositions |
| Wear resistance | Høj | Høj |
| Levetid | 8-10 years[1] | 8-10 years[1]Zirconia – up to 15 years |
| Æstetik | Metal shows through the ceramic (blue edge at the gingiva). | Absolute imitation of natural enamel |
| Care | Careful, with regular professional cleaning | Tight fit to the gum makes care easier |
| Biocompatibility | May cause allergies, galvanosis | Hypoallergenic, bioinert |
| Weight | Massive | Lightweight |
Dentures of what material to use, the doctor decides, after examination and information gathering.
Composites
Composite materials are mainly used in dental fillings. In orthopedics, composites are used in the fabrication of veneers. Thin plates are made on site and immediately placed on the teeth. Veneers do not correct defects, but mask them. Composite onlays are affordable, quick and easy to make. But they are quite fragile. Ceramic veneers last much longer and look better.
Of course, it is better to determine in advance, dentures from what material will suit you better. But it should be remembered that the final decision rests with the doctor. Based on his experience, knowledge and objective orthopedic picture, he will make the choice that will be optimal for you.
Remember, the best material for dentures is the one that suits you best.
[1] https://isma.ivanovo.ru/attachments/48611