Reading time ~ 6 min Number of readings: 5728
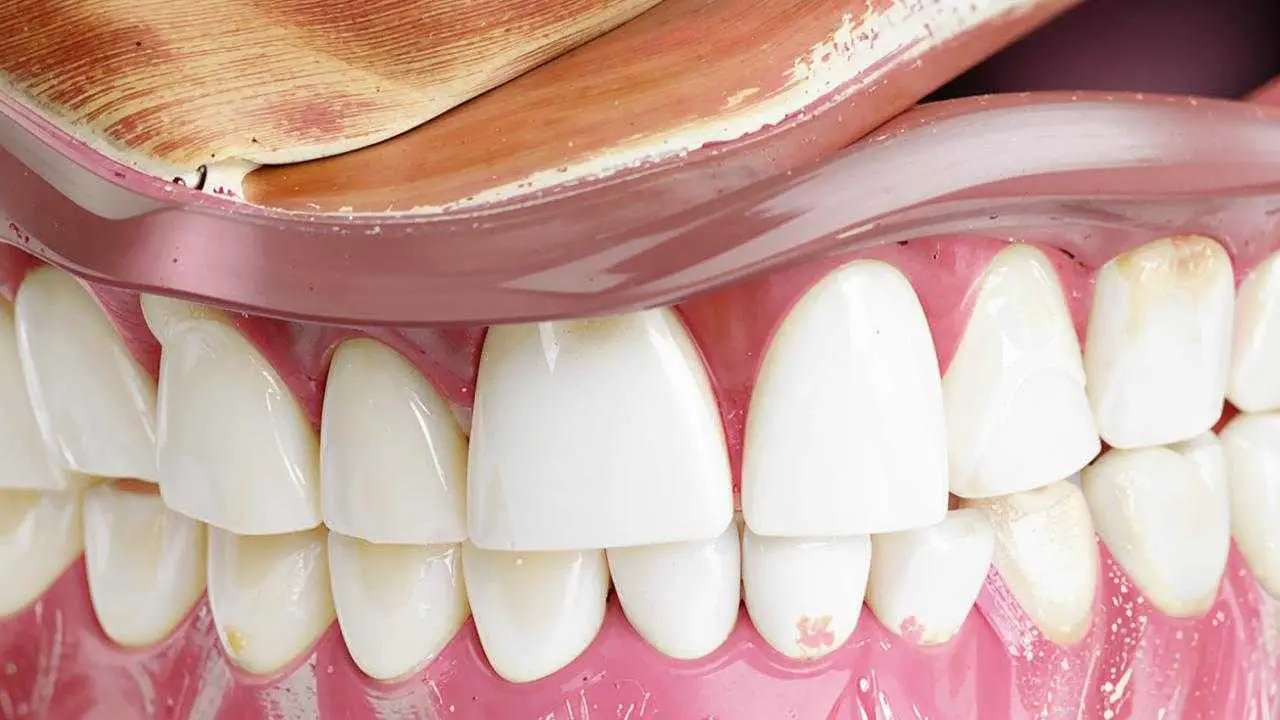
Caries is a non-infectious disease. It is characterized by the leaching of minerals from the hard tissues of the tooth and the formation of carious cavities. The initial degree is caries in the stain stage. At this stage, the disease can be treated with therapeutic methods, without a drill.
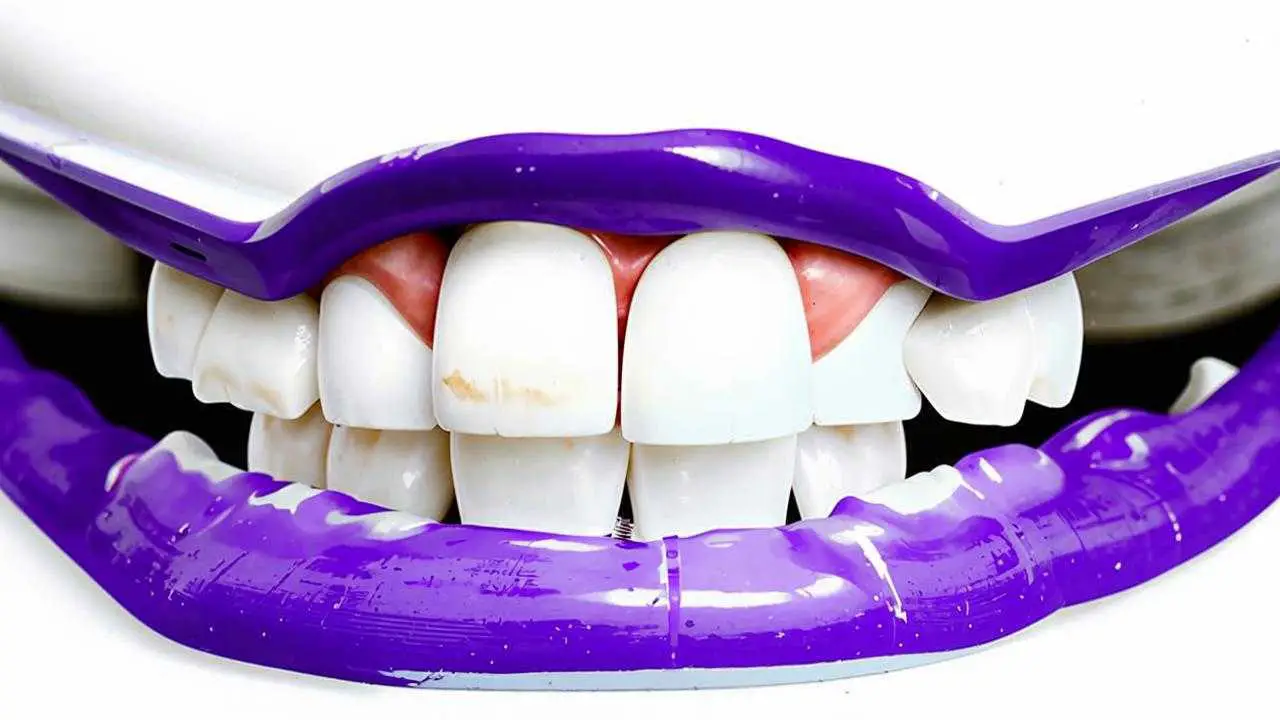
Unfortunately, the only sign of chalky caries is a spot on the enamel. It does not give painful sensations, only occasionally it can react to chemical irritants. There are no definite symptoms. It is difficult to see it, especially on the side teeth. Therefore, the initial caries in the stain stage often goes unnoticed. The doctor is consulted when the disease reaches the stage of medium or deep decay, involving the dentin and cementum of the tooth.
That’s why, it’s important to visit the dentist regularly. The doctor will not just see a chalky stain, he will make a differential diagnosis with other diseases, prescribe appropriate treatment.
Causes
Caries in the stain stage occurs due to various reasons. Among them we can highlight:
- Inadequate diet. Frequent, uncontrolled consumption of carbohydrates, fermented foods, sugars provides an ideal environment for the multiplication of bacteria.
- Lack of fluoride. Practice shows that saturating the water with fluoride reduces the number of infections.
- Vitamin deficiency. Vitamins are involved in many chemical processes, including mineralization of enamel.
- Decreased immunity. The body does not have enough resources to neutralize pathogens.
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Belching, increased acidity disturb the acid balance in the oral cavity. Acid becomes too much, it begins to destroy the enamel.
- Insufficient oral care. This is why tooth decay is so common in children and teenagers. They don’t have the patience to brush their teeth for 2 minutes, and kids don’t have the skills to do it correctly yet.
There are many other reasons, such as the density of saliva, violation of tissue formation, peculiarities of the structure of teeth, which also affect the frequency of caries development. However, the main ones remain the ones listed above.
Methods of diagnosing caries in the stain stage
The appointment begins with a conversation with the patient, the doctor collects information that will help to make a diagnosis. Dots of white color appear on the teeth in different diseases. It is important for the dentist to distinguish caries from a stain caused by fluorosis, hypoplasia, recently removed braces or improperly performed teeth whitening. This determines the treatment plan and its success. They are mainly distinguished by the nature of the stains: with caries they are uneven, but clearly delineated. Then proceed to the next stages of diagnostic examination:
The doctor pays attention to the state of the oral cavity, teeth. Checks the bite, palate, occlusion. Then proceeds directly to the teeth. Using a probe determines the foci of enamel softening, their area, depth. Tapping on the crown (percussion) gives an idea of the state of the tissues that hold the tooth in the hole. Palpation helps to determine whether the patient has enlarged lymph nodes, in what position are the salivary glands and ducts.
- Vital staining
If the doctor suspects caries in the initial stage, he performs a vital staining to confirm the diagnosis. In white spot stage caries, the enamel loses minerals (demineralizes) and the dye penetrates through the holes, staining the spots. Healthy areas do not change color.
Other types of diagnostics: X-ray, thermal test, electroodontometry in white caries on teeth are used rarely, by indication.
Treatment of caries in the white spot stage
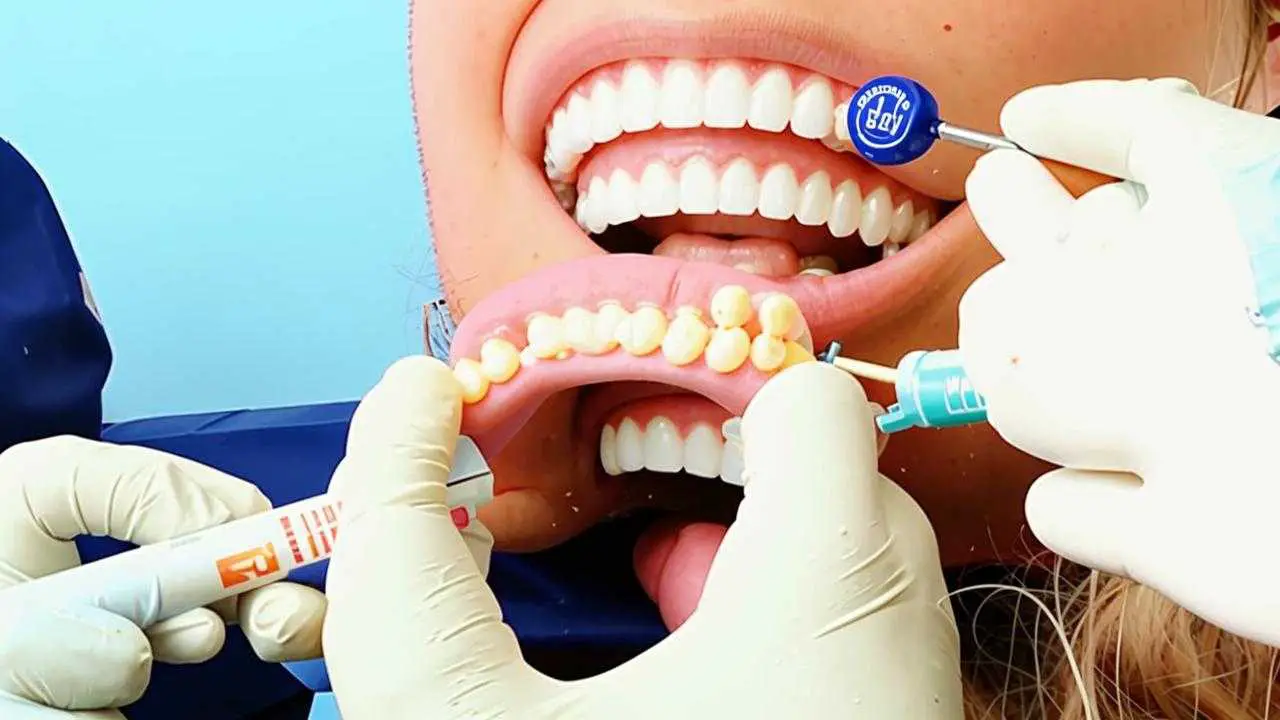
- The beginning of the disease is characterized by demineralization of enamel, its softening, friability within clearly delineated boundaries. Therefore, intervention begins with remineralization of the tooth surface. They carry out applications of medicines that contain minerals. After a course of 10-15 procedures, the enamel is strengthened enough to resist bacteria.
- Fluoridation. Fluoride ions protect the enamel from the influence of acids and prevent the penetration of bacteria.
- Silvering. In dentistry, there is no consensus on this procedure. Some doctors claim that it does not treat caries, but serves as a means of prevention. Others generally consider the procedure harmful. Others use it regularly and find it a good remedy.
- Icon technique. The tooth is etched with gel, treated with a special solution, and then a polymer is applied. Thus, as a result of one procedure, the doctor destroys the carious spot, saturates the enamel with minerals and seals all pores and cavities.
- Physical therapy. As a component of complex therapy use electrophoresis and phonophoresis with preparations of calcium, phosphorus, sodium fluoride and other trace elements.
- Diet. Limiting the use of carbohydrates, sugars, acids helps to accelerate recovery.
Before treatment, it is recommended to undergo a professional teeth cleaning.
During treatment, the dentist will select special toothpastes with a high content of fluoride and calcium. The doctor often prescribes pharmacy remedies for applications at home.
It can be dangerous to treat caries in the white spot stage on your own. Time is lost, the disease progresses and the tooth can be lost.
Complications
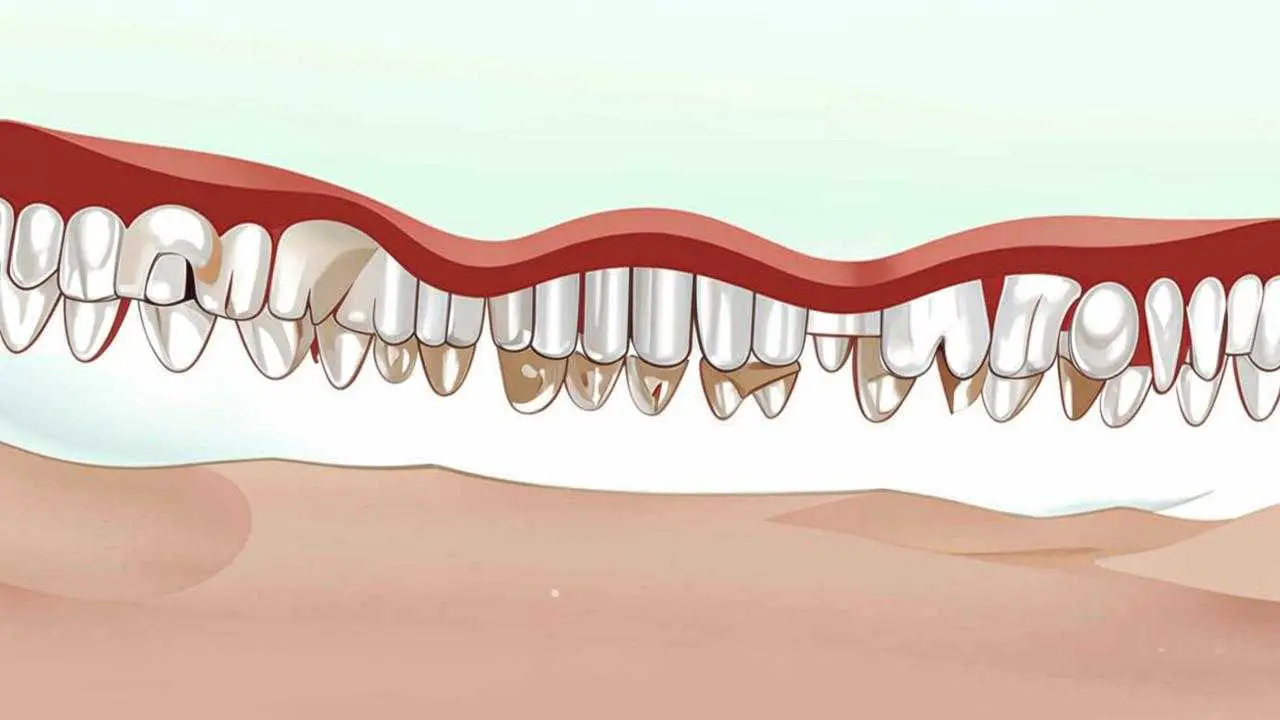
If you do not recognize the signs of infection in time, then pigments begin to penetrate through the porous enamel and a dark spot is formed in place of the white. Sometimes it darkens to black. To remove the infected layer you have to use a drill. If the microorganisms reach the dentin, more extensive preparation is done, but the treatment of superficial caries is still minimal and the tooth is finished with a simple filling.
In neglected cases, pathogens reach the pulp (nerve). Pulpitis develops. The nerve has to be removed, the canals are filled. This adversely affects the strength of the walls of the dental unit.
If the inflammation affects the root of the tooth and the surrounding tissues (most often happens in the case of neck caries), then periodontitis begins. It is dangerous in itself, because it often leads to tooth loss, but also because it provokes coronary artery disease [1] of the heart, endocarditis.
Preventive measures
Prevention of caries of the stain stage includes a set of simple but effective measures:
- From childhood, accustom the child to brush his teeth. First with help, then independently.
- Use the recommended toothpaste, floss.
- Have regular professional teeth cleanings
- Accept fluoridation if your doctor recommends it.
- Have fissure sealing as recommended by your dentist.
- Visit the dental clinic regularly for preventive checkups
- Eat foods low in sugar and limit fast carbohydrates.
Prevention of caries requires less time, effort and money than treatment of its consequences. Neglected caries leads to tooth loss and the need for prosthetics. At the same time, simple preventive measures will get rid of the appearance of carious spots on the teeth and provide a pleasant smile for many years.
Sources:
[1]https://www.health.harvard.edu/diseases-and-conditions/gum-disease-and-the-connection-to-heart-disease