Periodontal tissue diseases are the second most common dental pathology, second only to tooth decay. Almost everyone knows that bleeding gums when brushing teeth can be the first step to losing them. Not surprisingly, one of the frequent questions patients ask is how to treat bleeding gums.
The appearance of blood may be a consequence of excessive activity during hygienic procedures or evidence of the development of a serious pathology that requires treatment. Sometimes the cause is both dental problems and systemic – endocrine disorders, avitaminosis, pregnancy, etc. To understand why the gums bleed, prescribe a comprehensive treatment, only a doctor can.
Causes of bleeding gums
More often, bleeding gums are not a demonstration of seasonal vitamin deficiency, but a sign of periodontal pathology. The cause of the disease can be affected by decayed teeth, sharp edges of restorations, dentures, traumatizing the mucosa, overload of individual dental units when closing (improper bite). But the main factor that triggers the development of a serious disease is plaque, which provokes periodontal inflammation:
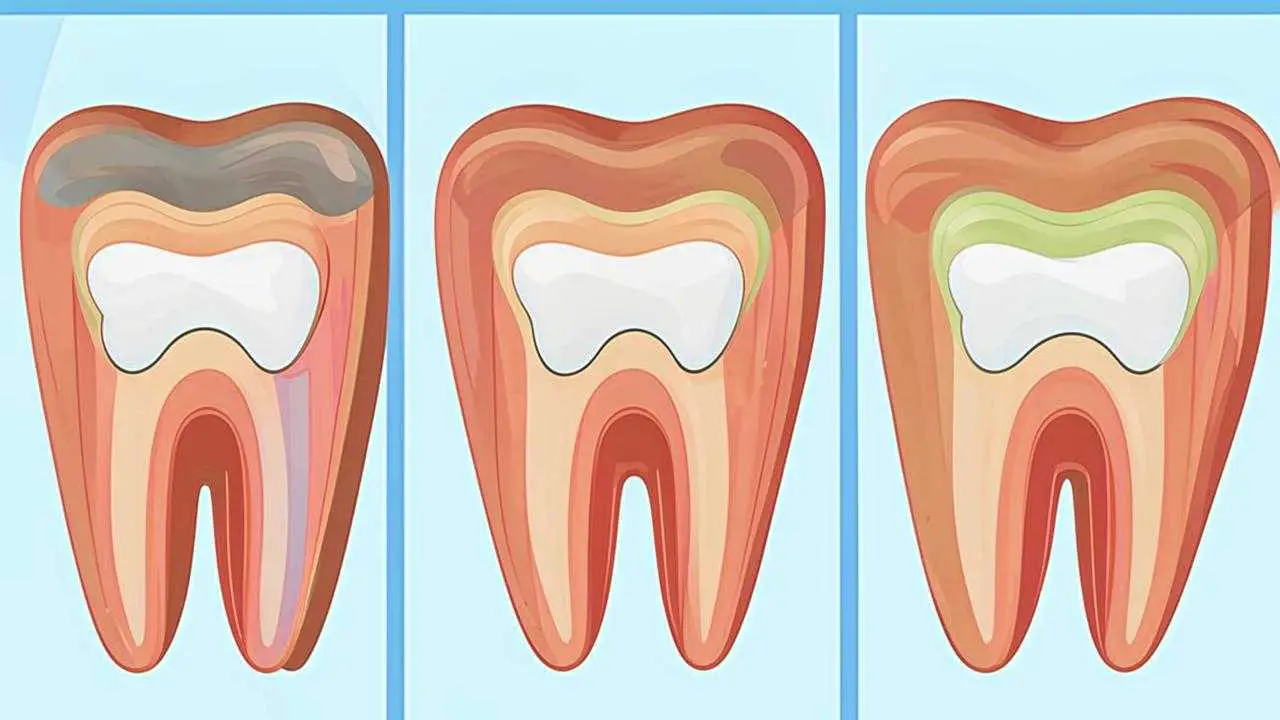
- Bacteria contained in plaque produce acids that are destructive to tooth enamel and periodontal tissues. Inflammation develops in the area of the gum margin – gingivitis. The mucosa swells, reddens, there is soreness. If you do not start treatment in time, the inflammation will penetrate deep into the tissue, destroying the tooth-gum attachment – periodontitis develops.
- In periodontitis, pockets are formed under the gum margin – depressions where bacterial plaque and food debris begin to accumulate. The developing inflammation damages the periodontal ligament, soft tissue, cementum, and alveolar bone. Usually 1 or more teeth are affected, less often there is a generalized form of the disease. In later stages of the disease, displacement of teeth is noted, their loss may occur.
- Periodontal disease is characterized by severe damage to the tissues surrounding the tooth. Bleeding gums are characteristic at the initial stage, later there is a different situation – the gums acquire a relatively healthy color, but there is a decrease in height, exposure of the roots of the teeth, their mobility.
In addition to dental pathologies, there are other causes of bleeding gums:
- Traumatic damage when using too hard toothbrush, eating hard, rough food (breadcrumbs, nuts, etc.);
- Systemic diseases accompanied by blood clotting disorders;
- endocrine disorders;
- chemical irritation – exposure to nicotine or other toxic substances;
- deficiency of vitamins K, C;
- reduced immunity;
- hormonal restructuring of the body during pregnancy, puberty, menopause.
Get rid of bleeding is possible only by eliminating the very cause of its appearance. Therefore, you can not ignore the alarming signs or use dubious “unconventional” methods for the treatment of periodontal pathologies.
Symptoms to which you need to pay attention
- Changes in the mucosa – redness (or blueing), swelling, increased sensitivity, soreness;
- appearance of blood every time you brush your teeth;
- Excessive dental deposits (plaque, calculus);
- رائحة الفم الكريهة
- gums become “loose”;
- the appearance of periodontal pockets;
- exposure of the necks of the teeth;
- mobility of dental units.
Bleeding gums in pregnancy
In most women, pregnancy develops inflammation of the gingival margin (gingivitis), manifested by increased bleeding. More often, it develops in the zone of the anterior incisors, canines, affecting the marginal part of the mucosa. The causes of this condition are hormonal restructuring of the body, calcium deficiency and a decrease in local immunity.
In pregnancy, the blood significantly increases the level of estrogen, progesterone, prostoglandin, which have a softening effect on tissues, including the periodontium. Gums become inflamed, increase in volume, there is increased bleeding. This condition is called gingivitis of pregnant women. If timely treatment is not started, harmful products of odontogenic microorganisms, penetrating into the bloodstream, can adversely affect the development of the fetus.
For the normal formation of the skeleton of the child needs a large supply of calcium, fluoride, vitamin D, other trace elements. Not surprisingly, pregnant women are at risk of calcium deficiency. If heavily bleeding gums in pregnancy in the 2-3 trimester, the reason is a lack of calcium in the body.
In the work of dentists today there are many effective, but at the same time completely safe for the pregnant woman and the fetus. Future moms are not only allowed, but even shown most hygienic procedures and types of dental treatment.
Bleeding with avitaminosis
Lack of useful substances is a problem for the entire body. Every organ and system needs vitamins, minerals, and the teeth and periodontal tissues are obliged to receive their part regularly. The immune system instantly responds to the lack of vitamins K, C, B group:
- Bleeding gums with a lack of vitamin C, occurs due to damage to the vascular walls. Also, the lack of this substance leads to a slowdown or cessation of collagen production – a component of connective tissue. And this is fraught with loosening of dental units, their falling out.
- Vitamin K regulates blood coagulation, its deficiency contributes to the appearance of bleeding.
Bleeding gums – a serious sign that requires a visit to the doctor. It does not appear on its own, but warns of the development of dental or systemic pathology, metabolic disorders. To get rid of the problem, you need to eliminate its cause and disposing factors. Dentists of ROOTT Clinic approach to the treatment of bleeding gums comprehensively, getting a good result.
التشخيص
Bleeding gums can be a sign of various diseases, and the task of the dentist to identify the exact cause of the pathological condition. Comprehensive diagnosis includes:
- Dental examination, during which the doctor will determine whether bleeding is associated with the presence of dental deposits.
- Orthopantomogram, computed tomography – allow to establish the type of destruction of the jawbone, assess the size, shape of periodontal pockets, collect information to make an optimal treatment plan.
If after the elimination of dental problems, bleeding does not stop, it is necessary to consult narrow specialists (therapist, endocrinologist, hematologist), additional studies (blood tests for sugar, hormones, blood coagulation, etc.).
Methods of treatment
Therapy is selected based on the general condition of periodontal tissues and the cause of pathological symptoms. In the presence of systemic diseases and endocrine disorders, the treatment of bleeding gums includes medication correction of the underlying pathology, symptomatic therapy is used – styptic drugs, vitamins K, C, to improve the rheological properties of blood and strengthen the vascular walls.
How to get rid of bleeding in gum disease? Complex therapy includes several stages:
- Hygienic cleaning and sanitation of the oral cavity. Dental deposits provide ideal conditions for the reproduction of pathogenic microorganisms that threaten the health of teeth and periodontal tissues. Mechanical, ultrasonic and Air Flow cleaning methods are used to remove dental deposits (plaque, calculus).
- Assessment of dental restorations and their correction – poor-quality fillings, crowns, dentures traumatize the mucosa, provide a good atmosphere for the development of inflammation. Such restorations should be replaced or corrected.
- Training in the proper care of teeth – the dentist recommends ways of cleaning, safe in the inflammatory process, will help you choose a brush, paste.
In some cases, hygienic cleaning is enough to eliminate the problem. Complicated situations, require medication, even surgical treatment:
- Rinsing the mouth with an antiseptic solution that helps to relieve inflammation, preventing infection of periodontal tissues. Rinse the mouth twice a day, the therapeutic course lasts 10-14 days.
- The use of local preparations with antiseptic, anti-inflammatory effect. The doctor will recommend an effective remedy against bleeding gums. Ointments and gels (Holisal, Acepta, Metrogil Denta, Apident-Aktiv, etc.) are applied to the gums with light massage movements 3-4 times a day.
- Symptomatic therapy – a course of antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs.
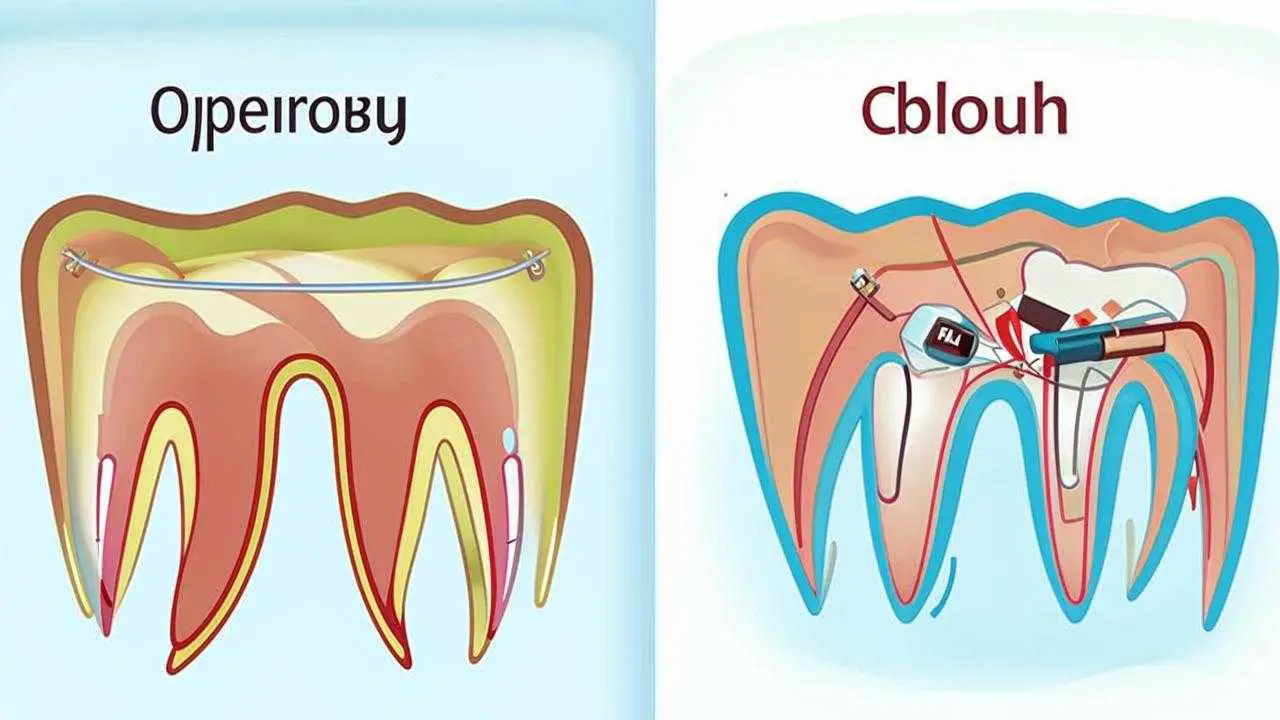
- Surgical periodontology – open curettage, flap operations in the most difficult cases (with granulation tissue overgrowth, deep periodontal pockets, tooth mobility). Vector” apparatus is also used for treatment of gum diseases.
Open and closed curettage of gums
The fastest way to get rid of bleeding contributes to the correction of diet – the exclusion of products that irritate the mucosa, limiting the consumption of carbohydrates. The diet should be dominated by products saturated with calcium, vitamins C, B, K.
Can be treated at home
Folk methods of treatment – mouthwash with decoctions of sage, cowberry leaves, oak bark, chamomile, are good for relieving inflammation and strengthening gum tissue only at the initial stage. With pronounced symptomatology means of phytotherapy are recommended only as part of a complex therapy. Plant remedies can reduce the manifestations of the disease, but do not eliminate dental deposits. Without professional hygienic cleaning, it is impossible to cure bleeding.
الوقاية
Prevention of periodontal disease consists in sufficient oral hygiene. Thorough daily hygiene, annual professional cleaning, will help to avoid the accumulation of plaque and calculus. And these are the main risk factors for the development of gum bleeding. Simple recommendations will help to maintain the health of teeth and periodontium, to avoid such an unpleasant symptom as bleeding.